Launching a project is like setting sail on a voyage; you have a destination (your goal), a map (your plan), and a crew (your team). But without instruments to check your position and course, you risk drifting off track or hitting unforeseen obstacles. In project management, the essential instrument for staying on course is the project tracker. Effective progress tracking is the compass that guides projects toward successful completion, ensuring deadlines are met, resources are managed, and goals are achieved.
This guide is designed for anyone looking to understand and implement robust project tracking system practices. We’ll explore what a project progress tracker is, why it’s indispensable, the core features to look for, how to set one up, and review some of the best project management trackers available today, including Morningmate. Whether you’re focused on tracking project tasks individually or managing multiple initiatives, mastering project tracking is key.
What Is a Project Tracker?
A project tracker is a tool or system used to monitor and report on a project’s progress against its plan. It centralizes information about tasks, milestones, timelines, resources, budgets, and risks.
Project tracking involves continuously monitoring activities, measuring performance against the project plan, and reporting progress to stakeholders. This includes collecting data on completed work, time taken, resources used, and costs incurred. By comparing this data to the initial plan, teams can determine if the project is on track, ahead, or behind schedule and budget. A project tracker, whether software or a visual board, facilitates this process.
Why Tracking Project Progress Is Crucial
Consistent and accurate progress tracking is fundamental to project success for several critical reasons. It provides essential visibility and transparency, offering a clear view of project status for the entire team and stakeholders, which builds trust. Tracking enables early issue detection, allowing managers to spot deviations like delays or budget overruns when corrective action is most effective. The data gathered forms the basis for informed decision-making regarding resources, priorities, and risks. Furthermore, tracking clarifies responsibilities and fosters accountability among team members. By comparing actuals to the plan, it facilitates improved forecasting of completion dates and costs. Trackers supply the necessary data for regular stakeholder communication through factual status reports. It also allows for objective performance measurement against baselines, identifying areas for improvement. Finally, visually tracking progress can significantly boost team motivation and momentum. Without effective tracking, projects operate blindly, hindering proactive management and alignment with objectives.
Core Features of a Good Project Tracker
While simple projects might be tracked with spreadsheets, more complex initiatives benefit immensely from dedicated project trackers, typically software tools. A good tracker should possess several core features:
Real-Time Progress Updates
The ability to see the current status of tasks and the overall project in real-time is paramount. This requires features that allow team members to easily update task statuses (e.g., Not Started, In Progress, Completed), log time spent, and mark milestones as achieved. The tracker should instantly reflect these updates, providing an accurate, up-to-the-minute picture of progress rather than relying on manually compiled weekly reports. This often involves cloud-based platforms accessible by the entire team.
Task and Resource Tracking
A fundamental requirement is the ability to list all project tasks, assign them to team members, set due dates, and track their status through completion. Beyond tasks, effective trackers often include capabilities for resource tracking. This might involve assigning resources (personnel, equipment) to tasks, monitoring workload distribution to prevent burnout or underutilization, and potentially tracking resource costs against the budget. Seeing who is working on what and their capacity is crucial for effective management.
Integration with Other Tools
Projects rarely exist in a vacuum. A good project tracker should integrate seamlessly with other tools the team uses daily. Essential integrations often include connections with communication apps like Slack or Microsoft Teams for notifications, syncing with calendars such as Google Calendar or Outlook, linking to file storage services like Google Drive or Dropbox for attaching documents to tasks, enabling task creation or updates via email, connecting with developer tools like Jira or GitHub for software teams, and linking to CRM/Sales tools to associate projects with customer data. These integrations reduce context switching and ensure information flows smoothly across platforms.
Custom Dashboards and Reports
Collecting data is not enough; the tracker must show it in a useful way. Good project tracking system tools have customizable dashboards and reporting features. Dashboards provide a clear visual summary of important project details. They show things like how many tasks are completed, the budget status, upcoming deadlines, and how resources are allocated. They use charts, graphs, and widgets to display this information.
Reporting features should let managers create detailed status reports and performance analyses. This includes comparing planned versus actual progress and summarizing resource use for different stakeholders. Real-time, customizable reporting helps with data-driven decision-making and clear communication.
How to Set Up a Project Tracker
Implementing a project tracker, whether it’s a sophisticated software tool or a simpler system, requires a structured setup process:
1. Define Clear Goals and Objectives
Before you can track progress, you need to know what you’re progressing toward. Start by clearly defining the project’s specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals and objectives. What does success look like for this project? What key results need to be achieved? This clarity provides the ultimate benchmark against which progress will be measured.
2. Create a Structured Project Plan
A successful tracker depends on a strong plan. Create a detailed project plan that includes a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to break down the project into manageable tasks. Include a complete task list, outline the dependencies between tasks, and provide realistic estimates for duration, effort, and cost. Clearly define resource allocation and develop a detailed schedule, often represented with a Gantt chart. This plan will serve as the foundation for what your tracker will monitor.
3. Establish Baselines and Milestones
After the initial plan, which includes the scope, schedule, and budget, is approved, set it as the baseline. The baseline is the original plan that will be used to measure all future progress and changes. In the schedule, pinpoint key milestones—important checkpoints that indicate major achievements, such as completing a phase or getting approval for a key deliverable. These milestones are essential for tracking overall progress. Your project tracker should enable you to enter and visualize these baselines and milestones effectively.
4. Regularly Update and Review Progress
A tracker is only effective when it has up-to-date information. Set a regular schedule for updating task statuses, logging time (if needed), and marking completed work. This could include daily check-ins or having team members update their tasks in the tracking tool throughout the day or week. Plan regular review meetings, such as weekly, to discuss the progress shown in the tracker, identify any differences from the original plan, address any obstacles, and make necessary adjustments to the plan.
5. Communicate Status with Stakeholders
UUtilize the information gathered in the project tracker to create regular status reports for stakeholders. Determine the frequency, format, and content of these reports according to the needs of the stakeholders. Dashboards in project tracking software offer real-time visibility, while formal reports summarize progress, highlight achievements, outline risks and issues, and predict completion dates. Consistent communication using data from the tracker ensures that everyone stays informed and aligned.
Best Project Tracker Tools
Numerous software tools are available to function as project trackers. The best choice depends on team size, project complexity, required features, and budget.
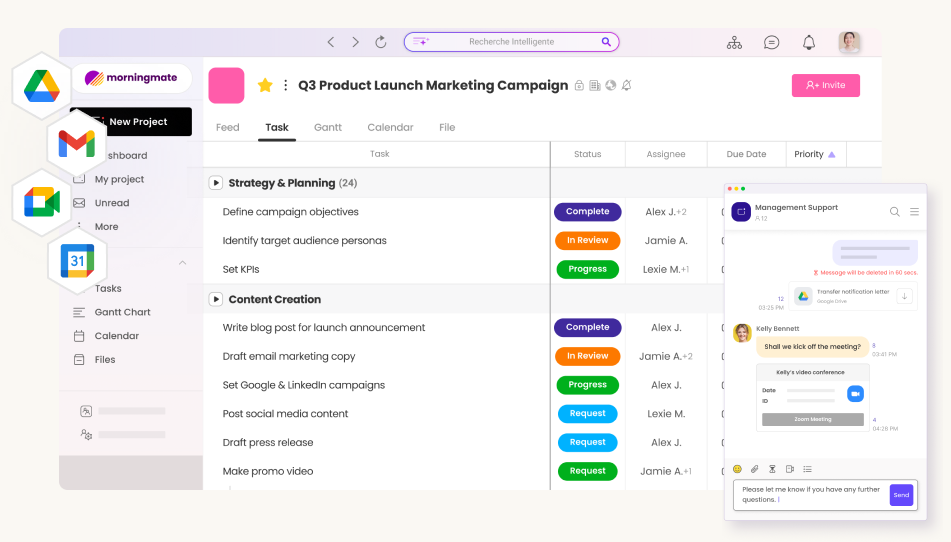
1. Morningmate: All-in-One Project and Progress Tracker
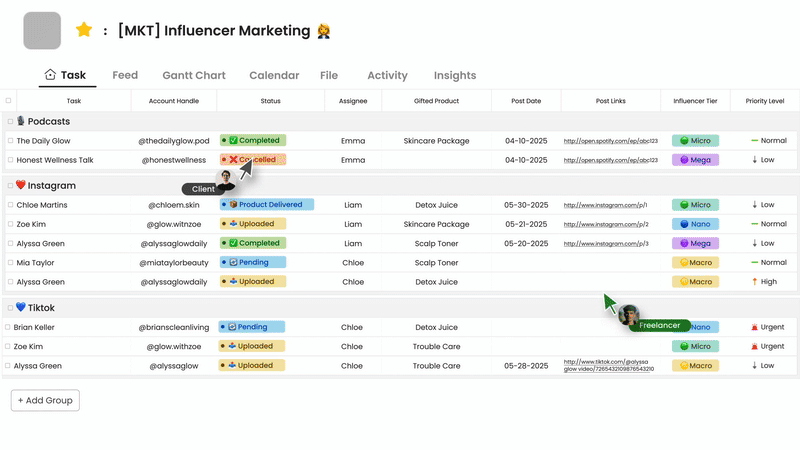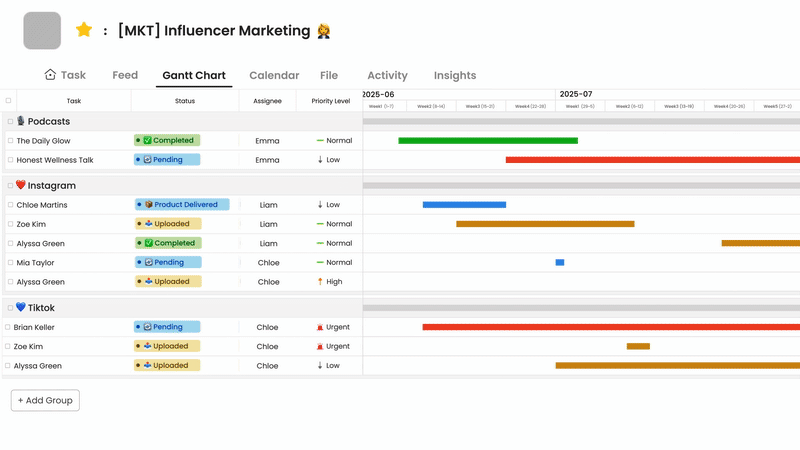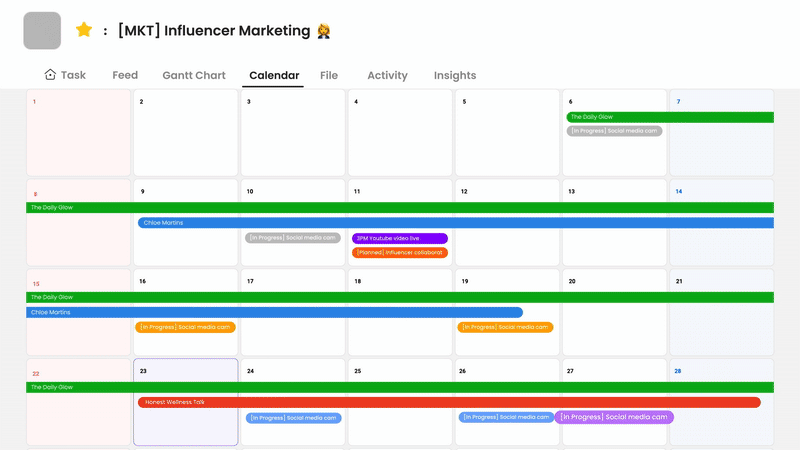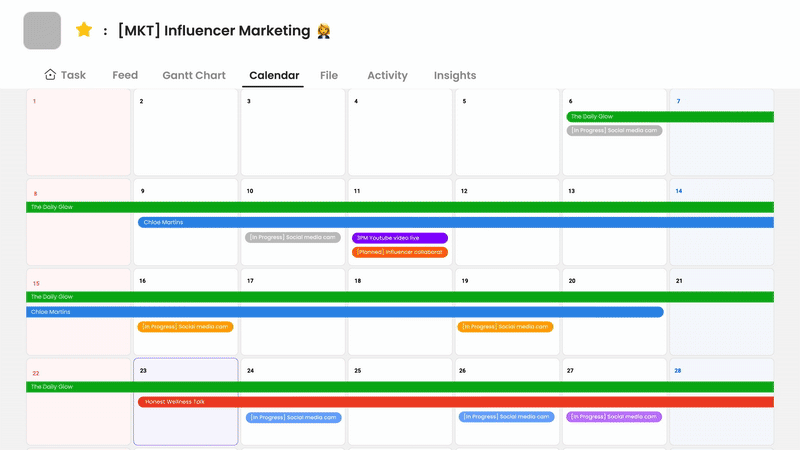
Morningmate is an excellent choice because it combines progress tracking with an all-in-one digital workspace that also supports communication and collaboration. This close integration is essential for providing real-time updates and a better understanding of tasks.
Its tracking features include task management through visual boards and lists, making it easy to update and see progress stages such as To Do, In Progress, and Done. You can track project tasks in detail with due dates, assigned team members, and subtasks, along with file attachments for relevant documents.
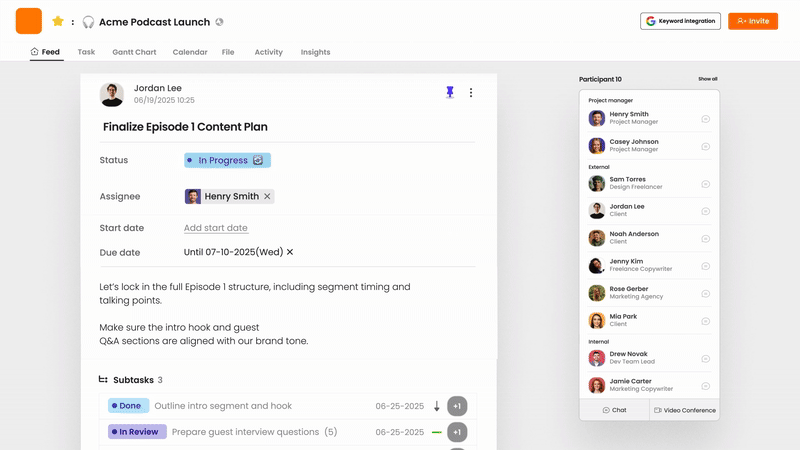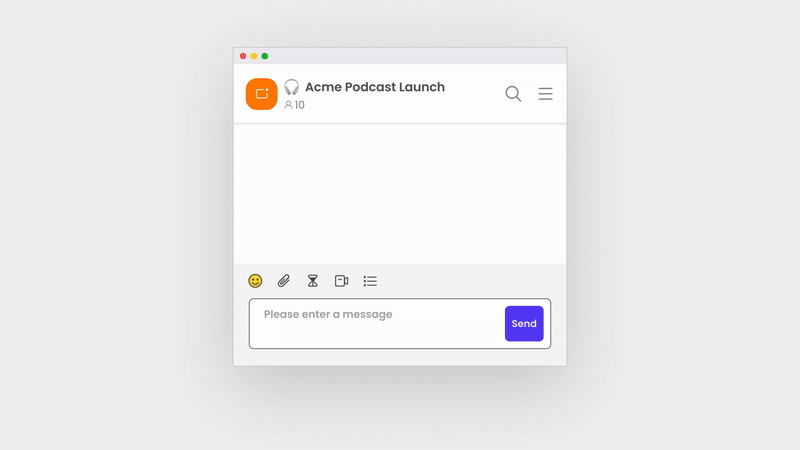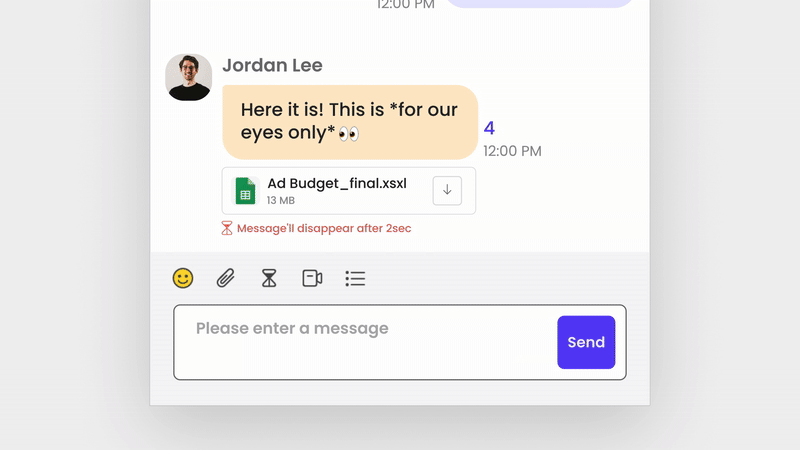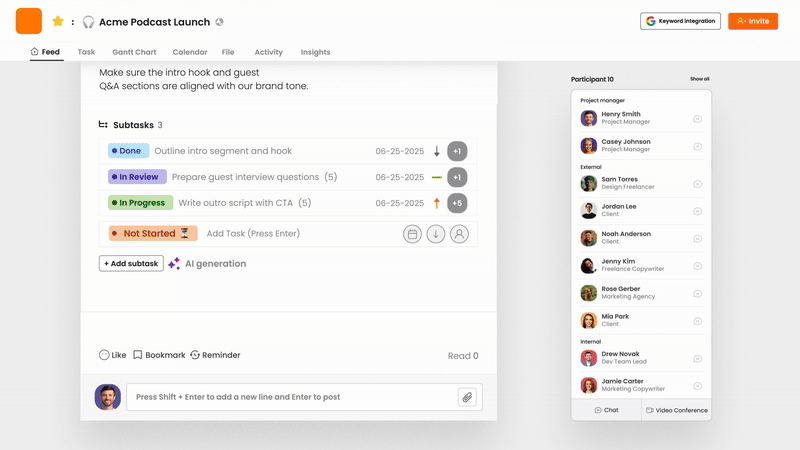
The platform’s main strength lies in merging tracking with real-time updates and communication. The feed-style interface and built-in messaging system allow for discussions about progress, questions, and challenges directly related to specific tasks, reducing delays between action and feedback. While the specific dashboard and reporting features may differ by plan, the structure supports gathering information, and potential AI features in paid plans could provide automated summaries. It also supports essential integrations with video conferencing and cloud storage.
By incorporating tracking into daily workflows and communication, Morningmate minimizes the challenges often faced when using separate tools for project management and chat. This leads to more consistent updates and offers a complete view of not only task status but also the conversations and context surrounding that progress. This makes it an outstanding project tracking system for teams that value a smooth workflow and real-time visibility.
2. Monday.com
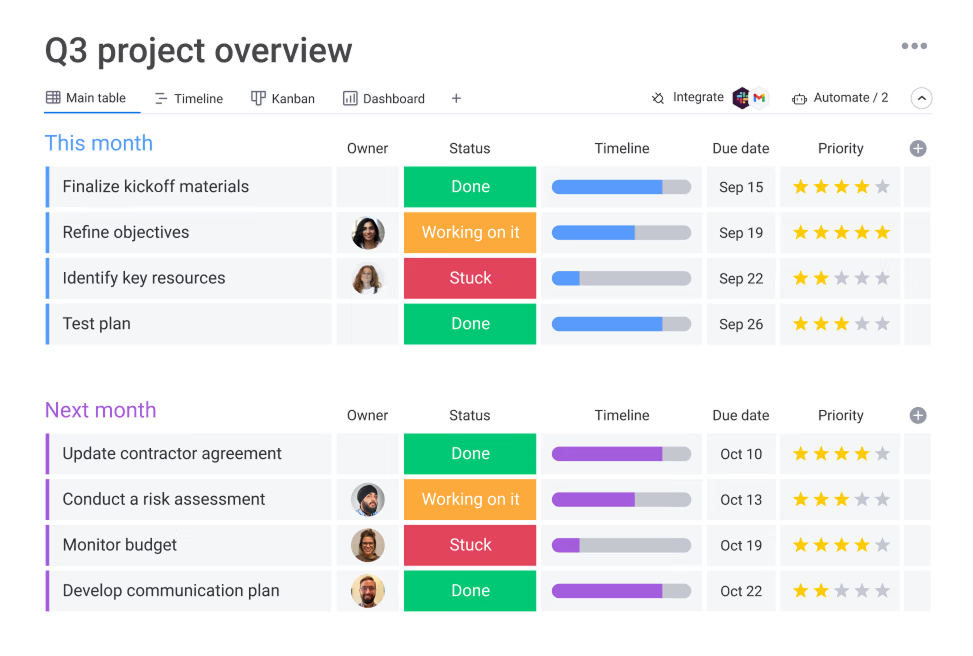
Monday.com is a highly visual and customizable Work OS often used for project tracking. Its tracking features include multiple views like Kanban, Gantt, Timeline, and Calendar for visualizing tasks and progress. Customizable columns enable tracking of various metrics such as status, priority, budget, and time spent, complemented by workload views for resource tracking. The platform provides highly customizable dashboards and reporting with diverse widgets (charts, numbers, progress bars) displaying real-time KPIs, resource allocation, and budget status across multiple projects. It also integrates with a wide array of third-party applications. Its main strength lies in the high degree of customization and the visual appeal of its dashboards.
3. Asana
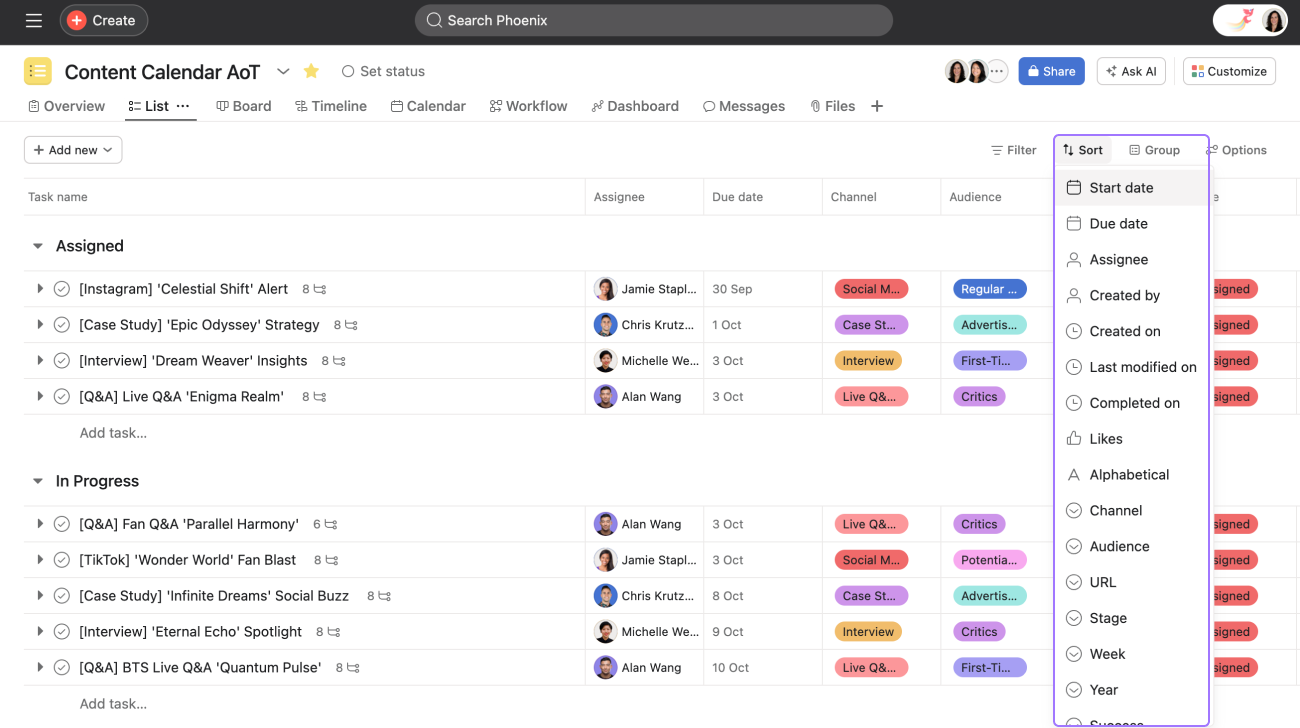
Asana is a popular project and task management tool focused on organizing and tracking work. For tracking, it offers robust task management with subtasks, assignees, due dates, and custom fields. Available views include List, Board, Calendar, and Timeline (often paid), with Workload features (paid) aiding resource allocation tracking. Asana provides project-level dashboards and reporting with customizable charts, though advanced or portfolio-level reporting usually requires paid plans. Portfolios enable progress tracking across multiple projects. Numerous integrations are available. Asana’s key strength is its powerful task management and workflow automation capabilities.
4. Smartsheet
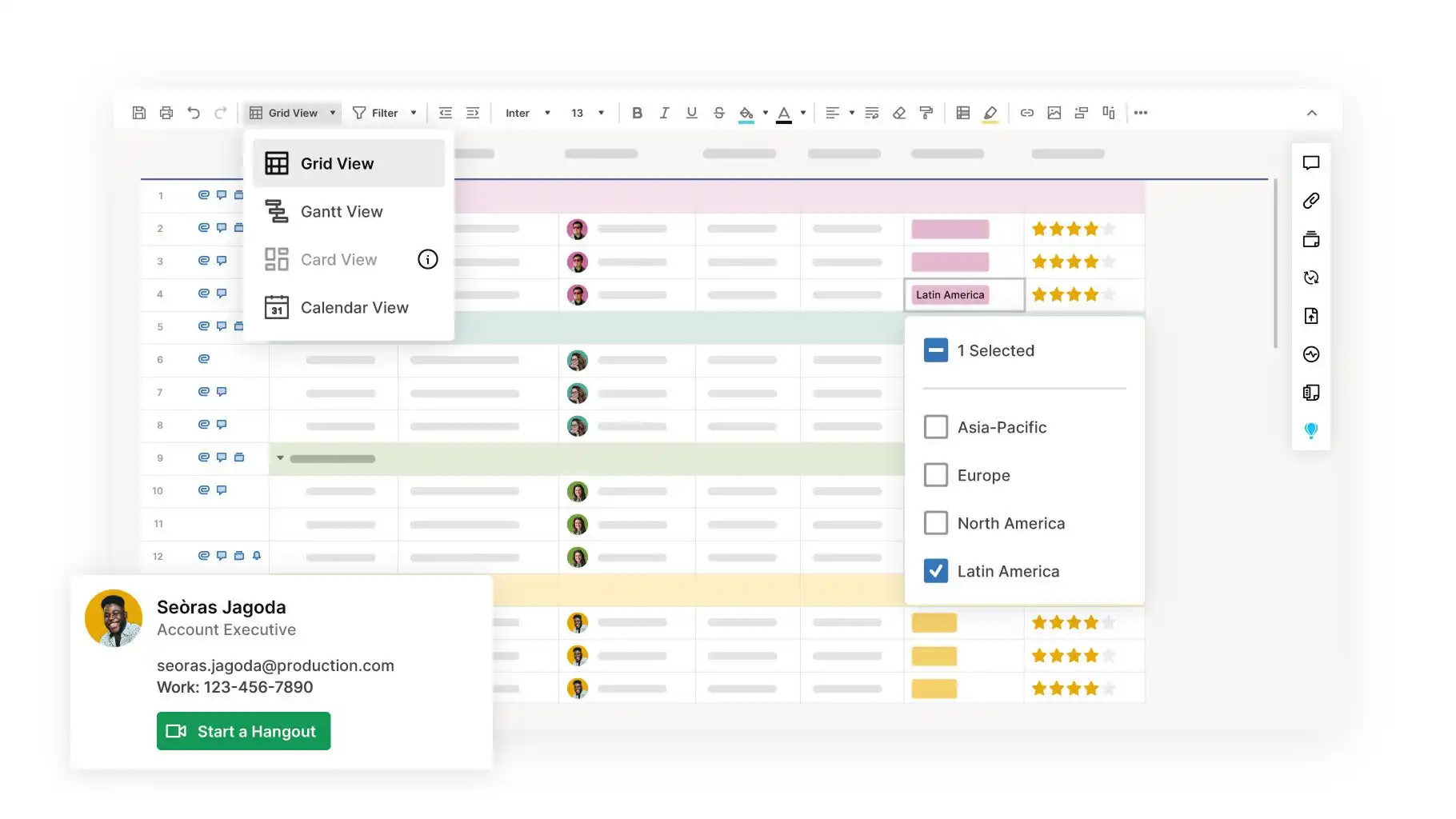
Smartsheet offers a powerful, spreadsheet-like interface enhanced with project management capabilities, making it familiar to many users. Its tracking features include Grid, Gantt, Card, and Calendar views for flexible monitoring. It supports task dependencies, critical path analysis, baselines, and resource management views. Strong formula capabilities allow for custom tracking calculations. For dashboards and reporting, Smartsheet enables the creation of customizable, widget-based dashboards pulling real-time data from multiple sheets and offers robust reporting to consolidate information. It integrates with major business applications. Its strength lies in powerful data handling and spreadsheet familiarity, making it suitable for complex scheduling.
5. Trello
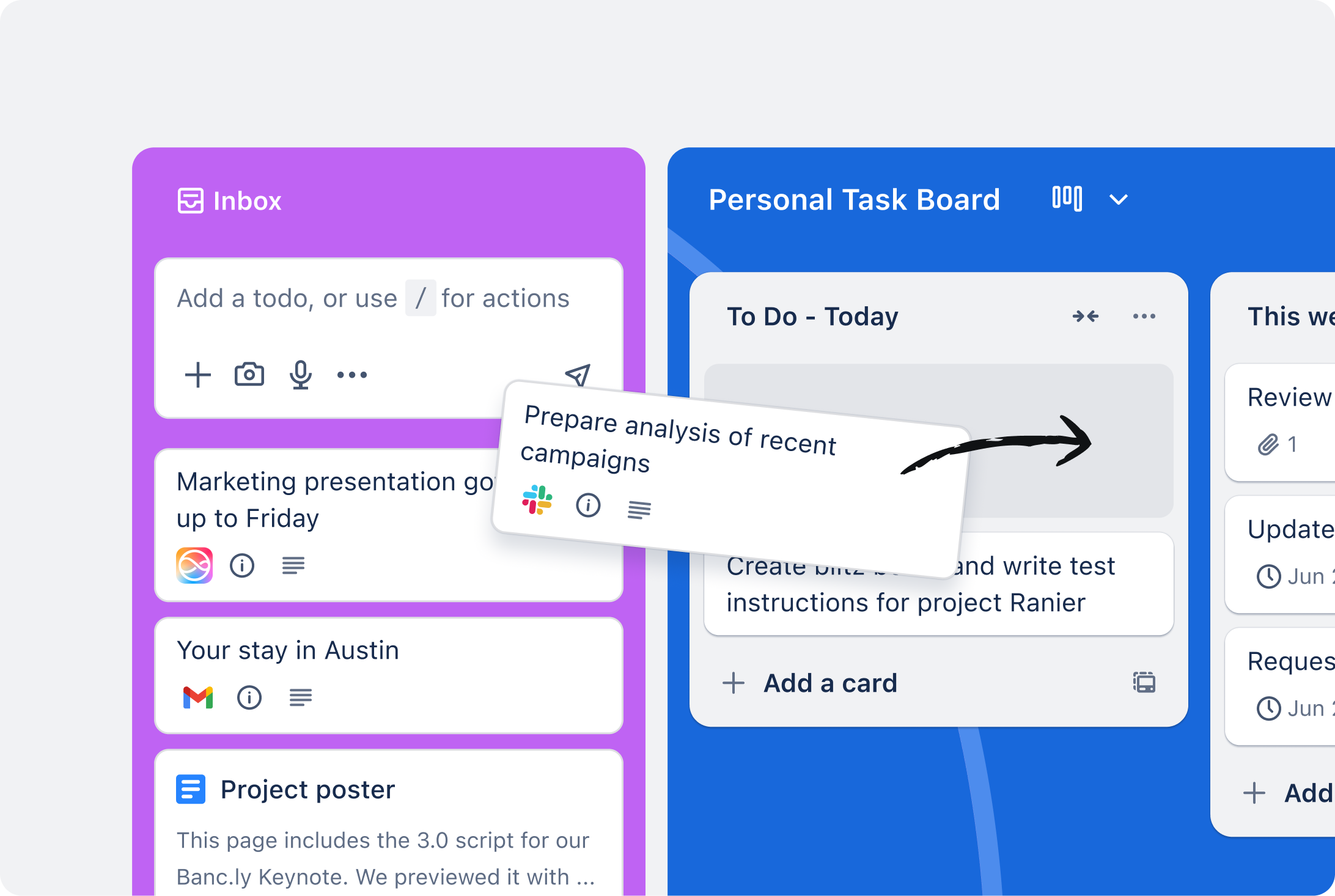
Trello is known for its simplicity and visual Kanban boards, making it very easy to learn and use for basic task tracking. Its tracking features primarily rely on Kanban boards where cards (tasks) move across lists (stages). Cards support due dates, checklists, assignees, and labels for status tracking, but native reporting and resource tracking are limited. Basic dashboards and reporting are available in paid plans, with more advanced capabilities typically requiring Power-Ups (integrations). Trello boasts an extensive library of Power-Ups for integration. Its strength is its simplicity, visual clarity, and ease of use for straightforward workflow tracking.
6. Wrike
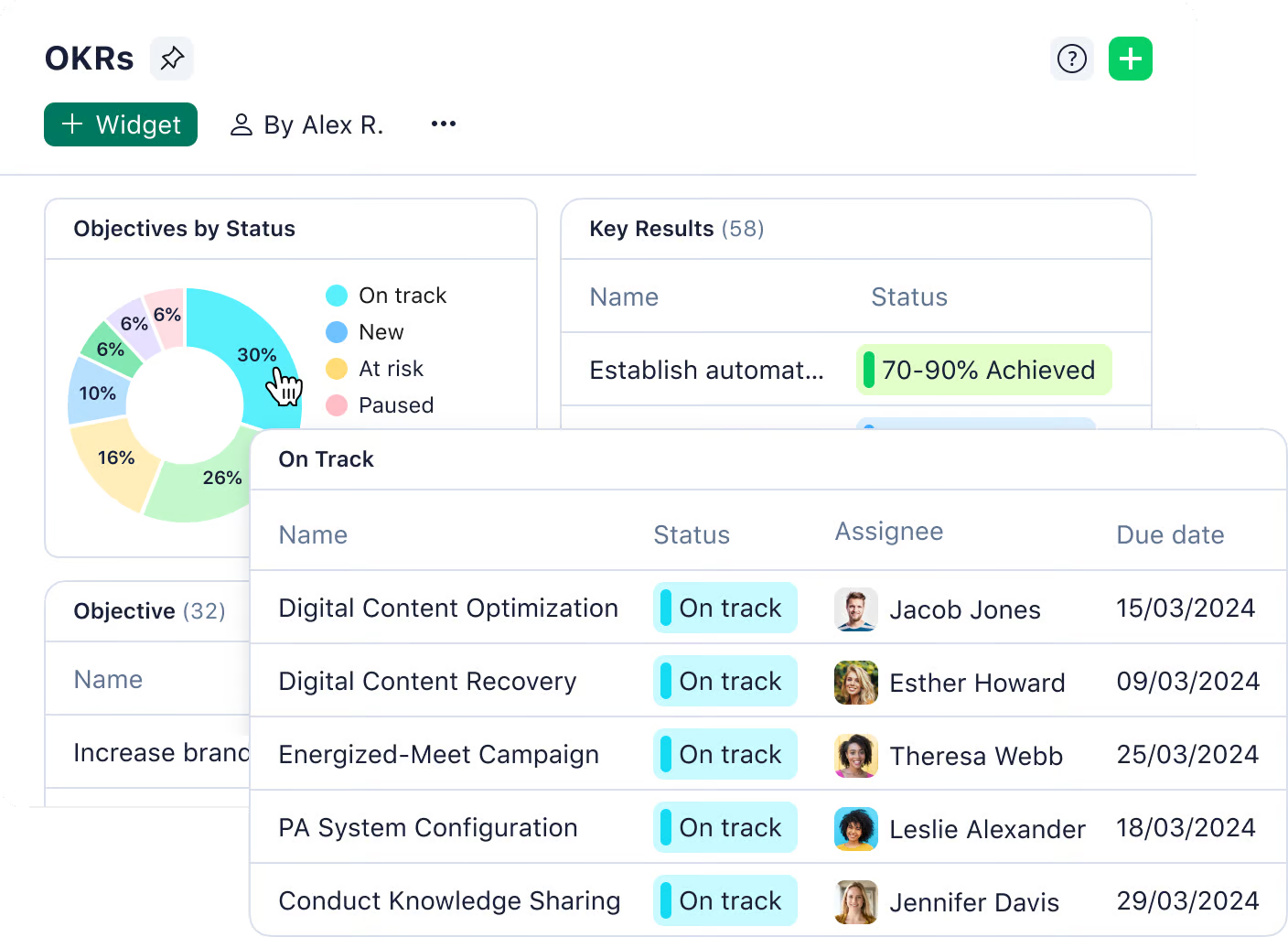
Wrike is a versatile work management platform designed for cross-functional collaboration and robust project tracking. Its tracking features encompass multiple views (Gantt, Kanban, tables, lists), task dependencies, time tracking, and resource/workload management views, with custom fields for detailed status monitoring. Wrike offers customizable dashboards and reporting, providing powerful, real-time capabilities across projects and portfolios, including budget tracking, performance analytics, and AI-powered risk forecasting. It integrates with a wide range of business tools. Wrike’s strength lies in its robust reporting, customization options, and suitability for complex projects and enterprise environments.
Strategies for Tracking Project Progress
Effective tracking involves looking at progress from different perspectives:
Tracking at the Individual Task Level
This granular level focuses on monitoring the status of each specific task outlined in the WBS. Key activities involve regularly performing status updates (Not Started, In Progress, Completed, Blocked), potentially logging effort or time spent against estimates, confirming deliverable completion meets requirements, and noting any issues or blockers encountered. Tools featuring clear task lists, Kanban boards, or detailed checklists are essential for managing this level effectively.
Tracking Overall Project Progress
This involves gathering data on individual tasks to assess the overall health of the project compared to its original goals. Common methods include milestone tracking (keeping an eye on the completion dates of important checkpoints), baseline comparison (comparing the current schedule and budget to the original plan using tools like Gantt charts or Earned Value Management), estimating the percentage complete (which can be subjective but is best based on objective measures), and regularly reviewing dashboards for a quick overview of key performance indicators such as task status, budget usage, and upcoming deadlines.
Managing Multiple Projects Simultaneously
For managers overseeing several projects, or for Program Managers, tracking necessitates a portfolio perspective. Effective strategies involve using portfolio dashboards provided by tools capable of summarizing status, health, resources, and risks across all relevant projects. Implementing standardized reporting formats across projects simplifies comparison and aggregation. Utilizing cross-project resource management tools helps manage shared resources and prevent conflicts. Regular prioritization reviews based on strategic alignment and performance are crucial. For formal programs, dedicated program trackers focusing on inter-project dependencies, risks, and benefit realization are employed.
How to Track Project Progress Effectively
Simply having a tracker isn’t enough; using it effectively requires discipline and smart practices:
Identify Risks Early
Treat your tracking data as an early warning system. By regularly reviewing task progress, budget expenditure, and resource allocation, you can spot potential deviations or bottlenecks before they escalate into significant problems. If a critical path task shows signs of slipping or costs are trending over budget, investigate immediately. Ensure your tracking process feeds information into your risk register and prompts timely risk assessment.
Standardize Reporting Formats
Consistency in reporting is vital, particularly when communicating with diverse stakeholders or managing multiple projects. Develop standard templates for status reports that consistently pull key metrics directly from your project tracker—such as tasks completed, upcoming milestones, budget variance, key risks, and outstanding issues. Standardization makes reports easier to generate, understand at a glance, and compare over time or across projects.
Use Milestones to Motivate Teams
Project tracking should not solely focus on identifying problems; it’s equally important to recognize achievements. Clearly define, communicate, and track progress toward key project milestones. Make a point to celebrate the completion of these significant checkpoints with the team. Visualizing progress and acknowledging these accomplishments can significantly boost morale, reinforce the value of accurate tracking, and maintain positive momentum throughout the project lifecycle.
Analyze and Document Lessons Learned
The data captured by your project tracker throughout the project is invaluable input for the lessons learned process. After project completion (or even at key phases), analyze the tracking data to understand what went well and what challenges arose regarding schedule adherence, resource estimation accuracy, risk occurrence versus planning, and overall task execution efficiency. Documenting these insights derived directly from tracked performance helps refine processes and improve planning for future projects.
Conclusion
Effective progress tracking is essential for successful project management. A well-designed project tracker gives teams the visibility they need to monitor tasks, manage resources, spot risks early, and make informed decisions. Whether you use a simple visual board or a more advanced project tracking system, the key principles are the same: set clear goals, create a solid plan with benchmarks, update progress regularly, and communicate effectively. Tools like Morningmate and others provide useful features to simplify this process. However, the real benefit comes from consistently tracking progress and using the insights gained to keep projects on the right path to success.