Are your projects always in a state of chaos? We understand the difficulty of transforming complex ideas into reality without a clear plan. While some may think that improvising saves time, we know that true efficiency stems from a well-structured approach.
This guide unveils effective techniques that truly make a difference. We cut through the clutter and show you how to achieve real results.
- The importance of project management techniques
- Traditional methods like Waterfall and CPM
- Agile approaches such as Scrum and Kanban
- And much more.
We aim to simplify your work. Morningmate helps you implement these techniques effortlessly, ensuring your projects stay on track from beginning to end.
| Technique/Methodology | Core Focus | Best For | Key Benefits |
| Waterfall Method | Linear, sequential phases | Projects with fixed requirements, construction | Clear structure, strong documentation, predictability |
| Critical Path Method (CPM) | Task dependencies, longest sequence of tasks | Scheduling complex projects, identifying critical path | Pinpoints crucial tasks, optimizes schedule |
| Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) | Breaking down large projects into smaller tasks | Defining project scope, ensuring all tasks are covered | Clear overview of deliverables, better resource allocation |
| Critical Chain Method (CCPM) | Resource dependencies, project buffers | Projects with limited resources, minimizing delays | More reliable completion dates, efficient resource use |
| PERT | Estimating uncertain task durations | Projects with high uncertainty, R&D | Realistic scheduling, improved risk management |
| Scrum | Iterative development, short “sprints” | Agile software development projects, evolving requirements | Fast delivery, continuous feedback, flexibility |
| Agile Framework | Values and principles (collaboration, adaptability) | Guiding philosophy for flexible project development | Encourages responsiveness to change, customer focus |
| Kanban | Visualizing workflow, limiting work in progress | Continuous flow, maintenance, support teams | Clear visibility, identifies bottlenecks, improved efficiency |
| Extreme Programming (XP) | High-quality software, intense collaboration | Small, co-located software development teams | Reduced defects, rapid feedback, adaptability |
| Adaptive Project Framework (APF) | Embracing uncertainty, continuous adjustment | Projects with high ambiguity, undefined outcomes | Adapts to change, maximizes client value |
| Event Chain Methodology | Analyzing events and their impact on schedule | Risk management for unpredictable projects | Proactive risk planning, dynamic scheduling |
| Extreme Project Management (XPM) | Rapid adaptation to highly uncertain environments | Innovative projects, R&D in volatile contexts | High flexibility, quick response to unforeseen issues |
| Hybrid Approaches | Blending traditional and Agile methods | Projects needing both structure and flexibility | Balances control and adaptability |
| Rational Unified Process (RUP) | Iterative development with a structured approach | Large software development projects, complex systems | Manages complexity, continuous refinement |
| Six Sigma & Lean | Quality improvement & waste reduction | Optimizing processes, enhancing efficiency | Higher quality outcomes, streamlined workflows |
What Are Project Management Techniques?
You might think “project management” is just about managing people and spreadsheets. In reality, it’s much more. Project management techniques are your secret tools for getting things done effectively.
These structured methods help you plan, execute, and keep your project on track. They guide you toward achieving your project goals and meeting deadlines. Without them, you risk losing control.
Tools vs. Techniques vs. Methodologies
Think of a project management methodology as your overall strategy—your comprehensive game plan. It’s a framework, like Agile or Waterfall, that guides the entire project lifecycle. Within that methodology, you’ll find specific project management techniques. These are the actions or processes you use to accomplish parts of your plan.
For instance, a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a technique used within various methodologies. Then there are project management tools, which are software applications that help you implement those techniques. Morningmate, for example, provides tools to apply your chosen techniques, from Gantt charts to project tracking.
Why They Matter in Every Project Lifecycle
Why should you care about project management techniques? The answer is simple: they bring order to chaos. Every project manager has faced tight deadlines or unexpected challenges.
Effective techniques help you manage projects by breaking them down into manageable parts, identifying critical tasks, and anticipating issues. They are essential for risk management, ensuring proper resource allocation, and keeping stakeholders informed.
Traditional Project Management Techniques
Some methods have endured for a reason. These project management techniques offer a structured, sequential approach.
Waterfall Method
The Waterfall method is one of the oldest project management techniques. It provides a clear, linear progression through project phases:
- Requirements: Define what needs to be built.
- Design: Plan how to build it.
- Implementation: Build it.
- Verification: Test it.
- Maintenance: Keep it running.
Each phase must be completed before the next begins. This method is ideal for software development or construction projects, where a rigid structure is beneficial.
Critical Path Method (CPM)
The Critical Path Method (CPM) helps project managers identify the longest sequence of tasks that must be completed on time for the entire project to finish as scheduled. It focuses on finding critical tasks—the ones that, if delayed, will push back the entire project timeline.
With CPM, you:
- Map out all project activities.
- Determine their task dependencies.
- Identify critical tasks.
This allows for strategic resource allocation. Project network diagrams can provide a clear visual representation of these paths, making critical path analysis straightforward.
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): Breaking Down the Beast
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is your blueprint for success. It takes a large, complex project scope and breaks it down into smaller, manageable components. Think of it as a detailed family tree for tasks.
The WBS helps you define:
- All the tasks
- Project activities
- Deliverables
This clarity helps the project team understand their roles and responsibilities. This effective technique ensures that no tasks are overlooked and that resource allocation is accurate. Morningmate’s Workspaces can help you create and manage your WBS, providing a clear overview of all tasks needed for project completion.
Critical Chain Method (CCPM)
The Critical Chain Method (CCPM) builds on CPM but adds a twist: it focuses on resource dependencies and buffers. While CPM identifies the critical path of tasks, CCPM considers the availability of project resources, such as personnel or equipment.
This method protects the project timeline from delays caused by resource bottlenecks, ensuring efficient use of resources and more reliable completion times.
PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique)
PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) is another powerful project management technique, especially for projects with uncertain activity durations. It uses a three-point estimate for each task to create a more realistic project schedule:
- Optimistic: The best-case scenario.
- Pessimistic: The worst-case scenario.
- Most Likely: The most probable scenario.
This approach helps gauge the likely project completion time and assess risks. While it may seem complex, PERT provides a clearer picture of project performance and aids in risk mitigation by highlighting potential delays.
Agile and Iterative Project Management Techniques
Agile project management moves away from traditional methods, embracing flexibility and continuous adaptation. This approach is ideal for projects where requirements may change or evolve.
Scrum: Sprinting to Success
Scrum is a widely-used Agile methodology that divides complex projects into smaller, manageable segments known as “sprints.” A sprint is a brief, time-limited period, typically lasting 1-4 weeks, during which a project team focuses on completing specific tasks.
Key components of Scrum include:
- Product Backlog: A prioritized list of features and requirements.
- Sprint Backlog: Tasks selected for a specific sprint.
- Daily Scrums: Short, daily meetings for the team to discuss project progress.
- Sprint Review: A demonstration of completed work to stakeholders.
- Sprint Retrospective: A reflection on the sprint to identify areas for improvement.
Scrum enables teams to remain adaptable and responsive to change, particularly in software development. It fosters strong communication and facilitates frequent delivery of working software.
Agile Framework (Agile Manifesto)
The Agile Framework is not a single technique but a collection of guiding principles, famously outlined in the Agile Manifesto. It challenges the rigidity of traditional methods by prioritizing people and adaptability.
The four core values are:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools.
- Working software over comprehensive documentation.
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation.
- Responding to change over following a plan.
These principles shape our approach to project development, encouraging a culture of rapid feedback and iterative delivery while emphasizing the human element in project success.
Kanban: Visualizing Your Workflow
Kanban is a visual project management technique that helps teams manage their workflow. It focuses on visualizing work, limiting work in progress, and maximizing efficiency. Kanban boards, divided into columns representing different stages of a task’s journey—such as “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done”—are commonly used.
Benefits of Kanban include:
- A clear visual representation of work.
- Identification of bottlenecks in the project management process.
- Improved flow of project tasks.
- Enhanced team communication.
Morningmate’s flexible workflow views make it easy to implement Kanban boards, providing your project team with a quick overview of progress. This helps project managers maintain visibility across their teams.
Extreme Programming (XP)
Extreme Programming (XP) is an Agile methodology focused on delivering high-quality software quickly. It emphasizes continuous improvement and close collaboration within the development team.
XP practices include:
- Pair Programming: Two developers work together at one workstation.
- Test-Driven Development (TDD): Writing tests before coding.
- Continuous Integration: Regularly merging code changes.
- Small Releases: Frequently delivering working software.
XP helps teams reduce defects and effectively respond to changing requirements, making it a powerful technique for software projects.
Adaptive Project Framework (APF)
The Adaptive Project Framework (APF) is an iterative approach designed for projects with high uncertainty and evolving requirements. Unlike traditional methods that require a clear project plan upfront, APF embraces change.
With APF, project managers and teams:
- Anticipate changes throughout the project lifecycle.
- Continuously review and adjust the project plan.
- Focus on delivering maximum value to clients.
This approach excels in situations where the final outcome is not entirely clear from the start, allowing teams to adapt and realign for project success.
Change Management and Hybrid Methodologies
Not every project fits neatly into a single methodology. Sometimes, blending different project management techniques or focusing on managing inevitable changes is necessary. This is where change management and hybrid methodologies come into play, offering flexibility and resilience for complex project development.
Event Chain Methodology
Event Chain Methodology enhances risk management by analyzing how specific events—both positive and negative—might impact project schedules and performance. It considers external factors and potential disruptions that can affect project tasks and their dependencies.
This technique utilizes:
- Event Chains: Sequences of events that can alter the project path.
- Probabilistic Scheduling: Modeling how events could affect the project timeline.
It provides project managers with a dynamic view of potential outcomes, enabling proactive risk mitigation planning.
Extreme Project Management (XPM)
Extreme Project Management (XPM) is tailored for complex projects operating in uncertain or rapidly changing environments. Unlike traditional methods that seek to control every variable, XPM recognizes that complete control is often unattainable.
In XPM, the project team focuses on:
- Rapid adaptation to change.
- Learning throughout the project.
- Maintaining flexibility in the project plan.
This approach is particularly effective for innovative projects or those with ambiguous objectives, emphasizing responsiveness to emerging situations.
Hybrid Approaches
Why limit yourself to one project management methodology when you can combine the best of both worlds? Hybrid approaches blend elements from traditional and Agile techniques to create a customized project management process.
Common hybrid models include:
- Water-Scrum-Fall: Using Waterfall for initial phases (like detailed requirements) and Scrum for development.
- Agile with WBS: Applying Agile sprints within a larger Work Breakdown Structure framework.
This allows project managers to leverage the structure of Waterfall while benefiting from the adaptability of Agile.
Rational Unified Process (RUP)
The Rational Unified Process (RUP) is an iterative software development methodology. While it shares some characteristics with Waterfall (having distinct phases), it emphasizes continuous feedback and refinement through iterations.
RUP’s key features include:
- Iterative Development: Progressing through cycles of development.
- Use-Case Driven: Focusing on user needs and scenarios.
- Architecture-Centric: Prioritizing a stable software architecture.
It helps development teams manage complexity and integrate new requirements throughout the project lifecycle, ensuring the final product meets the evolving needs of stakeholders.
Six Sigma & Lean
While not exclusively project management techniques, Six Sigma and Lean principles are often integrated to enhance project performance and achieve success.
- Six Sigma: Aims to reduce defects and variation in processes to achieve near perfection, using data-driven approaches for consistent quality.
- Lean: Focuses on eliminating waste (anything that doesn’t add value) from the project management process, streamlining workflows, and optimizing resource allocation.
Combining these methodologies can lead to significant improvements in efficiency and quality, resulting in faster project completion and better outcomes. They provide powerful frameworks for continuous improvement in any project development effort.
Key Project Planning Techniques
A well-laid plan is the foundation of project success. These project planning techniques help project managers visualize, organize, and strategize before a single project task even begins.
Gantt Charts
Gantt charts are perhaps the most popular project management tools for visualizing a project schedule. They provide a clear visual representation of tasks against a timeline. Each bar on the chart represents a project task, showing its start date, end date, and duration.
Gantt charts help us:
- See the project timeline at a glance.
- Track project progress.
- Identify task dependencies.
- Understand resource allocation over time.
Morningmate features intuitive Gantt chart timelines, allowing you to encapsulate task details in one view. This makes it simple to lay out dependencies and distribute work efficiently, ensuring all the tasks are aligned and on time.
Project Network Diagrams
Project Network Diagrams (sometimes called PERT charts, though distinct) offer a different way to visualize project activities and their dependencies. They use nodes to represent tasks and arrows to show the flow and sequence between them. This helps us see the critical path and understand how one task’s delay impacts others.
These diagrams are great for:
- Identifying the critical path.
- Understanding complex task dependencies.
- Optimizing the sequence of project tasks.
They’re a powerful tool for project managers to analyze the logic of their project plan.
Resource Planning Charts: Who Does What, When?
Resource Planning Charts are crucial for effective resource management. They provide a visual representation of how project resources (people, equipment, budget) are allocated across different project activities and over time. This helps prevent over-allocation or under-utilization of your valuable project team members.
With these charts, we can:
- Optimize resource allocation.
- Prevent bottlenecks.
- Ensure team members aren’t overworked.
They are essential for making sure you have the right people and tools available at the right time to achieve project objectives.
RAID Log and Risk Registers: Spotting Trouble Early
Effective project risk management is about anticipating and mitigating potential issues. A RAID Log (Risks, Assumptions, Issues, Dependencies) and Risk Registers are vital project planning techniques for this.
- RAID Log: A simple document to track key elements that can impact project success.
- Risk Registers: Detailed records of identified risks, including their likelihood, impact, and risk mitigation planning.
These tools help project managers proactively identify and address potential problems before they escalate.
Choosing the Right Tool or Technique
Selecting the right project management techniques and project management tools is crucial for project success. It’s not about finding a magic bullet, but rather the perfect fit for your unique project development.
Match Techniques to Project Type
The first step is to consider the nature of your project development. A great project management technique for a construction project might fall flat for a software rollout.
- Predictable Projects: For clear, stable requirements (like building a bridge), traditional methods like Waterfall or CPM shine. You know the finish line.
- Adaptive Projects: If requirements evolve or the environment is uncertain (think new product development), Agile methodologies like Scrum or Kanban offer the flexibility you need. They help your project team pivot quickly.
- Highly Complex Projects: For ventures with many unknowns or high risk, Event Chain Methodology or Extreme Project Management (XPM) can provide the necessary foresight and adaptability.
We always recommend assessing your project scope and inherent predictability before committing to a methodology.
Consider Team Size and Stakeholders
The size of your project team and the number of project stakeholders also play a big role.
- Small Teams: Agile frameworks often work well for smaller, co-located teams that can communicate frequently and adapt fast.
- Large Teams: Larger, distributed teams might benefit from more structured approaches or hybrid models that provide clearer communication channels and reporting.
- Stakeholder Involvement: If project stakeholders need frequent updates or want to be deeply involved, iterative techniques that offer regular reviews can be ideal. If they prefer less involvement until key milestones, traditional methods might fit better.
Morningmate helps bridge communication gaps, no matter your team size. Our communication features ensure seamless discussions and feedback, keeping everyone informed and engaged.
Evaluate Tool Features and Flexibility
Finally, assess the project management tools themselves. Do they support the project management techniques you’ve chosen?
Look for:
- Gantt charts and project network diagrams for visual planning.
- Features that support resource management and task dependencies.
- Customization options to fit your specific project management process.
- Reporting capabilities for tracking project progress and project performance.
Morningmate offers a comprehensive platform with AI capabilities and integrations to support a wide range of project development techniques. From customizable dashboards to detailed activity logs, we provide the tools to effectively manage projects and ensure your project plan stays on track.
Popular Project Management Tools to Know
You’ve got the techniques down, but how do you put them into action? That’s where project management tools come in. These platforms help you organize project tasks, track project progress, and collaborate with your project team. We’ll show you some top contenders.
Morningmate

We might be biased, but Morningmate offers a truly unique approach to project management. It’s built to bring culture and visibility to your ideal workspace. We combine powerful project development techniques with an intuitive, social media-style interface. This helps your team adopt it quickly and keep communication flowing.
Morningmate features include:
- Workspaces & Posts: Organize project tasks and discussions in dedicated spaces, similar to a social feed. This makes it easy to track activity and get real-time updates.
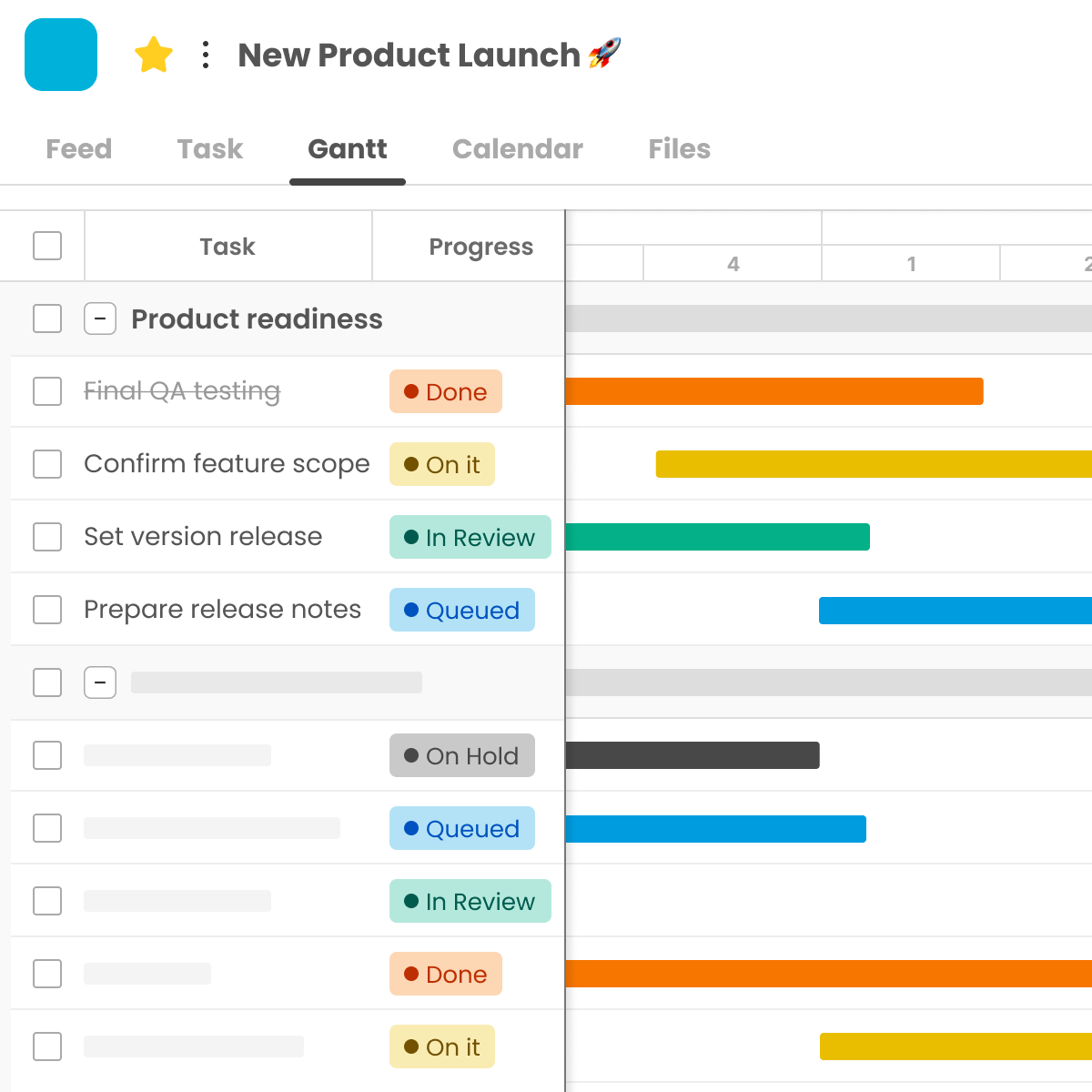
- Gantt Chart Timelines: Visualize your project schedule, lay out task dependencies, and ensure all the tasks align for project completion. It’s simple to use and incredibly effective.
- Personal Dashboard: Customize your view with useful widgets to see what matters most to you, from assigned project tasks to bookmarked posts.
- AI Capabilities: Our new AI capabilities help streamline workflows and automate routine project management process elements, freeing up your project team for more impactful work.
- Seamless Communication: Built-in chat and integrations with tools like Zoom and Microsoft Teams keep your project stakeholders and team members connected, alleviating common work pains.
We’ve seen how Morningmate helps teams like production and creative groups meet their project plan goals, even in the fast-paced world of complex projects. It truly transforms intricate responsibilities into neatly organized solutions.
Asana
Asana is a widely-used project management tool that offers great flexibility in organizing tasks. It helps teams track project tasks and manage workflows effectively. You can view projects in various formats, such as lists, boards, and timelines, allowing you to adapt to different management styles.
Asana enables teams to:
- Manage tasks and subtasks efficiently.
- Set deadlines and assign responsibilities.
- Monitor project progress through dashboards.
While it excels in task tracking, larger and more complex projects may require additional customization.
Trello
Trello employs a Kanban-style board system, making it visually appealing and easy to use for many teams. Each “card” represents a task, and you can move cards across lists (e.g., To Do, Doing, Done) to track progress.
Trello is particularly good at:
- Organizing tasks simply.
- Visualizing workflows.
- Facilitating quick collaboration on smaller projects.
It’s an excellent choice for less complex projects or teams that prefer a straightforward visual approach.
Jira

Jira is a robust project management tool, especially favored by development teams for software projects and Agile methodologies like Scrum and Kanban. It offers powerful features for bug tracking, issue management, and customizable workflows.
With Jira, you can:
- Create and track “issues” (tasks, bugs, stories).
- Configure detailed workflows for any project management process.
- Generate comprehensive progress reports.
While it is highly capable, its extensive features may present a steeper learning curve for new project managers.
Monday.com
Monday.com offers a highly visual and customizable platform for project management and team collaboration. It provides various views, including Gantt charts, Kanban boards, and tables, making it adaptable to many project development methods.
Monday.com helps teams:
- Visualize tasks and workflows.
- Manage resource allocation with workload views.
- Automate repetitive tasks for greater efficiency.
It serves as a centralized hub for project stakeholders and team members to manage all project activities.
Best Practices for Implementing Project Management Tools and Techniques
Adopting new project management tools and techniques can significantly enhance your project development. However, simply purchasing software is not enough. True project success comes from effective implementation. Here’s how to do it right.
Start with Process Mapping
Before selecting any tool or technique, map out your current project management process. Clearly define how your team handles tasks, communication, and decision-making.
Process mapping helps you:
- Identify critical tasks and workflows.
- Spot bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
- Understand your existing strengths and weaknesses.
With a clear picture, you can choose tools and techniques that genuinely address your challenges, ensuring any new approach improves your project activities.
Standardize Documentation
Consistency is essential for a smooth project lifecycle. Standardizing documentation ensures that everyone on the team knows where to find information and how to record it. This applies to project plans, progress reports, risk management logs, and communication.
- Templates: Use consistent templates for briefs, meeting minutes, and status updates.
- Centralized Storage: Keep all project resources and documents in one accessible location. Morningmate’s centralized content features make this easy, so you never lose track of important information.
- Clear Naming Conventions: Ensure files and folders are logically named.
Standardized documentation facilitates smooth transitions, reduces confusion, and significantly enhances project performance by saving time and effort.
Train Teams Consistently
Even the best project management tools are ineffective if your team doesn’t know how to use them properly. Consistent and thorough training is essential for successful adoption.
- Onboard Training: Provide initial training for new software and techniques.
- Ongoing Support: Offer continuous learning opportunities and refreshers. Morningmate provides onboarding training and direct support from real people, ensuring your team masters the platform.
- Feedback Loops: Encourage team members to share feedback on what works and what doesn’t, then adapt your training accordingly.
This approach helps your team develop strong project management skills and confidently apply new techniques to achieve project objectives.
Master Project Management with Morningmate
We’ve explored various project management frameworks and Agile approaches. Choosing the right techniques is crucial for any team aiming for project success.
Key Takeaways:
- Project management techniques differ from tools or methodologies.
- Traditional methods provide structure, while Agile offers flexibility.
- Hybrid approaches combine the best of both worlds.
- Planning tools like Gantt charts are vital for visualization.
- Selecting the right technique depends on your project, team, and stakeholders.
Morningmate empowers you to apply these project management techniques seamlessly. We provide the tools to simplify project planning, track progress, and keep your team connected, ensuring your next project is a resounding success.




