Does your organization hum with the energy of shared ideas and seamless teamwork, or does it often feel like talented individuals are working in parallel universes? Achieving effective Workplace Collaboration is more than just putting people in the same room (or virtual meeting); it’s about creating an environment where the collaboration of employees becomes the engine driving innovation, efficiency, and engagement. When teams truly connect, share knowledge freely, and work towards common objectives, the results can be transformative.
This guide provides actionable strategies and insights for businesses aiming to enhance teamwork and productivity. We’ll define what true workplace collaboration looks like with real-world examples, explore its profound benefits, identify common roadblocks, and outline best practices. We’ll also look at the digital tools that underpin modern collaboration efforts, including platforms like Morningmate, and discuss the crucial role of leadership in cultivating a truly collaborative culture.
What Is Collaboration in the Workplace?
Understanding the essence of collaboration is the first step towards fostering it effectively within your teams.
Definition and Core Concepts
Workplace Collaboration is the active process where two or more employees, teams, or even departments work together cohesively towards achieving a common goal. It goes beyond simple cooperation (dividing tasks and working separately) and involves:
- Shared Understanding: Aligning on objectives, roles, and expectations.
- Open Communication: Freely exchanging information, ideas, and feedback.
- Mutual Respect & Trust: Valuing diverse perspectives and relying on each other’s contributions.
- Shared Responsibility: Collectively owning the process and the outcome.
- Synergy: Combining individual strengths to produce a result greater than the sum of its parts (1+1=3).
Effective collaboration requires intentional effort and the right environment to flourish. It’s about collective intelligence in action.
Examples of Effective Collaboration at Work
Collaboration isn’t just a buzzword; it manifests in tangible ways:
- Cross-Functional Project Teams: Marketing, sales, and product teams working together to launch a new product, ensuring messaging, features, and sales strategies are aligned from the start.
- Brainstorming & Ideation Sessions: Diverse groups coming together to generate creative solutions for a business challenge, actively listening and building on each other’s ideas without judgment.
- Peer Review & Feedback Loops: Developers reviewing each other’s code, writers getting feedback from designers, or marketers sharing campaign drafts for input before launch, leading to higher quality output.
- Shared Knowledge Bases: Teams contributing to internal wikis or shared documentation platforms (like Notion or within a PM tool) to ensure critical information is accessible to everyone, reducing redundant questions and onboarding time.
- Agile Stand-ups & Retrospectives: Teams quickly syncing on progress, identifying blockers, and collectively reflecting on how to improve their processes in the next iteration.
Why Is Workplace Collaboration Important?
Investing in fostering collaboration of employees isn’t just about creating a pleasant work atmosphere; it delivers significant strategic advantages.
Key Benefits for Teams and Organizations
- Increased Productivity & Efficiency: Teams that collaborate well avoid duplicated work, resolve issues faster, and leverage shared knowledge, leading to quicker project completion and better resource utilization.
- Improved Problem Solving & Decision Making: Bringing diverse perspectives and expertise together results in more comprehensive analysis of problems and more robust, well-rounded solutions.
- Enhanced Quality of Work: Feedback loops, shared expertise, and collective ownership contribute to higher quality deliverables and services.
- Greater Adaptability: Collaborative teams can navigate change and uncertainty more effectively, quickly adjusting strategies and workflows based on shared understanding and open communication.
- Better Resource Management: Visibility into workloads and shared goals allows for more effective allocation of tasks and resources across the team or organization.
Impact on Employee Engagement and Innovation
- Higher Engagement & Morale: Employees who feel connected to their colleagues, believe their contributions are valued, and work in a supportive environment are generally more engaged, motivated, and satisfied with their jobs. Collaboration fosters a sense of belonging.
- Accelerated Learning & Development: Team members learn from each other constantly, sharing skills and knowledge organically, which accelerates individual growth and builds collective capability.
- Increased Innovation: Collaboration is a powerful catalyst for innovation. When ideas from different viewpoints collide and are built upon in a trusting environment, novel solutions and creative breakthroughs are more likely to emerge.
Challenges to Workplace Collaboration
Despite its benefits, achieving seamless collaboration often faces hurdles. Recognizing these is crucial for addressing them.
Silos and Poor Communication
Organizational structures often create departmental silos where teams operate independently, hoarding information and developing an “us vs. them” mentality. Communication channels may be fragmented, unclear, or underutilized, leading to misunderstandings, delays, and a lack of awareness about related initiatives. Remote and hybrid work can exacerbate these communication challenges if not managed proactively with the right tools and practices.
Lack of Shared Goals or Transparency
When teams or individuals lack clarity on overarching goals or how their work contributes to the bigger picture, motivation to collaborate diminishes. A lack of transparency regarding project status, decision-making processes, or resource allocation can breed mistrust and confusion, further hindering effective teamwork. If individuals don’t see the shared benefit or understand the context of their collaborative tasks, they are less likely to engage fully.
Best Practices to Improve Collaboration Among Employees
Cultivating a collaborative environment requires deliberate actions and consistent effort.
Promote Open Communication
- Establish Clear Channels: Define which tools are used for specific types of communication (e.g., chat for quick questions, project feeds for updates, email for formal external communication).
- Encourage Active Listening: Train and encourage team members to listen attentively and seek to understand others’ perspectives before responding.
- Foster Psychological Safety: Create an environment where employees feel safe to speak up, share ideas (even unconventional ones), ask questions, and admit mistakes without fear of negative consequences.
- Regular Check-ins: Implement regular team meetings (like daily stand-ups or weekly syncs) focused on alignment, progress, and removing blockers.
Set Shared Goals and Clear Roles
- Define Common Objectives: Ensure every team member understands the team’s or project’s primary goals and how their work contributes.
- Clarify Roles & Responsibilities: Use frameworks like RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) charts to clearly define who does what, avoiding confusion and duplicated effort.
- Visualize Progress: Use shared dashboards or project boards to make progress towards shared goals visible to everyone.
Create Opportunities for Team Building
- Cross-Functional Projects: Assign projects that require collaboration between different teams or departments to break down silos and build relationships.
- Social Activities: Organize informal virtual or in-person events (team lunches, coffee breaks, games) to help colleagues connect on a personal level, building rapport and trust.
- Shared Learning: Encourage participation in workshops or training sessions together.
Recognize Collaborative Efforts
- Acknowledge Team Wins: Celebrate successes achieved through teamwork, not just individual accomplishments.
- Highlight Collaborative Behaviors: Publicly or privately recognize individuals who actively help colleagues, share knowledge, or facilitate group problem-solving.
- Incorporate Collaboration in Performance Reviews: Consider teamwork and collaborative contributions as part of performance evaluations.
Digital Tools That Support Team Collaboration
Technology plays a vital role in enabling modern workplace collaboration, especially for distributed teams.
Messaging and Video Tools (e.g. Slack, Zoom)
- Instant Messaging (Slack, Microsoft Teams): Essential for quick questions, real-time updates, and reducing email clutter. Channels help organize conversations by topic or project.
- Video Conferencing (Zoom, Google Meet, Microsoft Teams): Crucial for face-to-face interaction, complex discussions, presentations, and building rapport in remote/hybrid settings. Features like screen sharing and whiteboarding enhance collaborative sessions.
Document Sharing & Real-Time Collaboration
- Cloud Storage (Google Drive, Dropbox, Box, OneDrive): Provide centralized access to files, ensuring everyone works from the latest version. Granular sharing permissions are key for security.
- Real-Time Co-editing (Google Docs/Sheets/Slides, Microsoft 365 Online): Allow multiple users to work on the same document simultaneously, speeding up content creation and review cycles. Version history tracks changes.
Project Management Platforms (e.g. Morningmate, Trello, Asana)
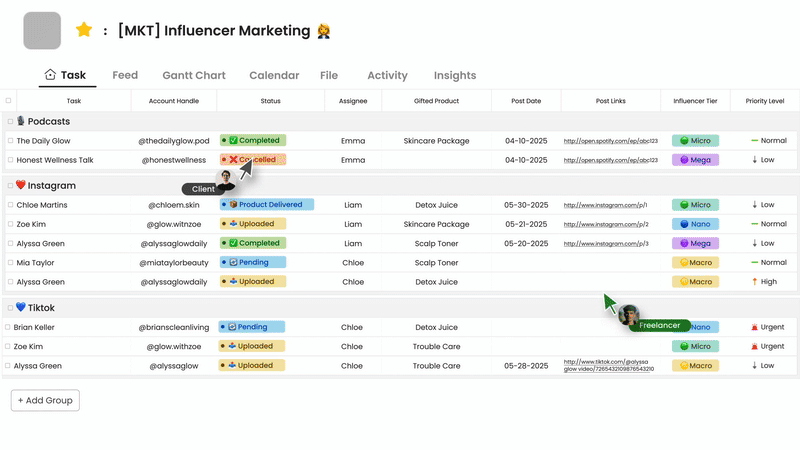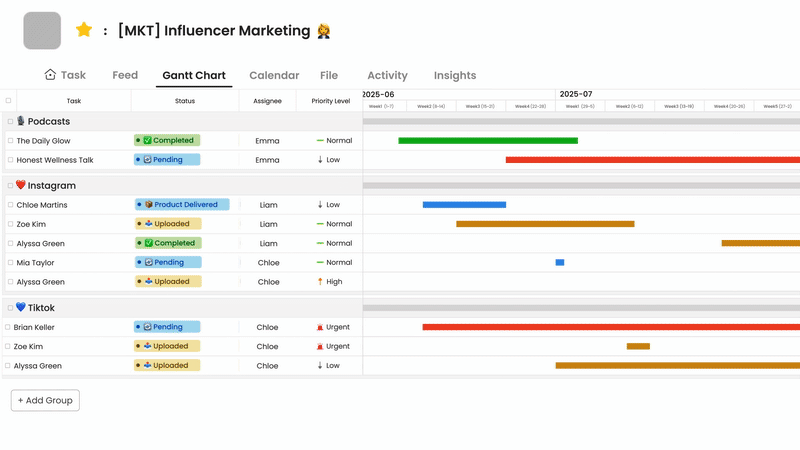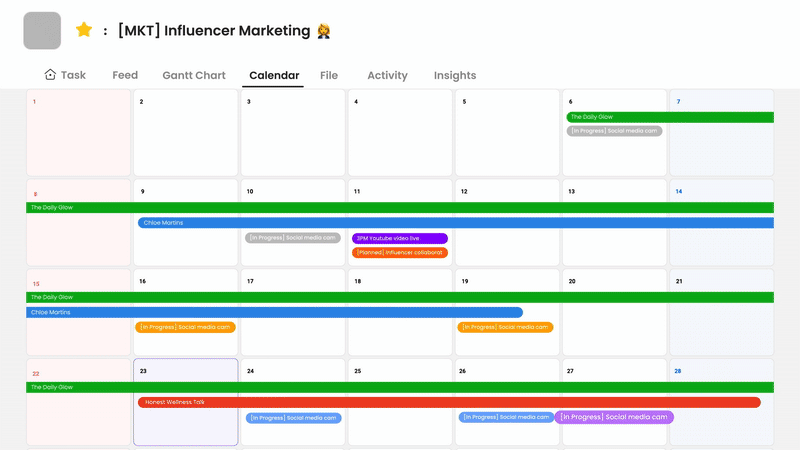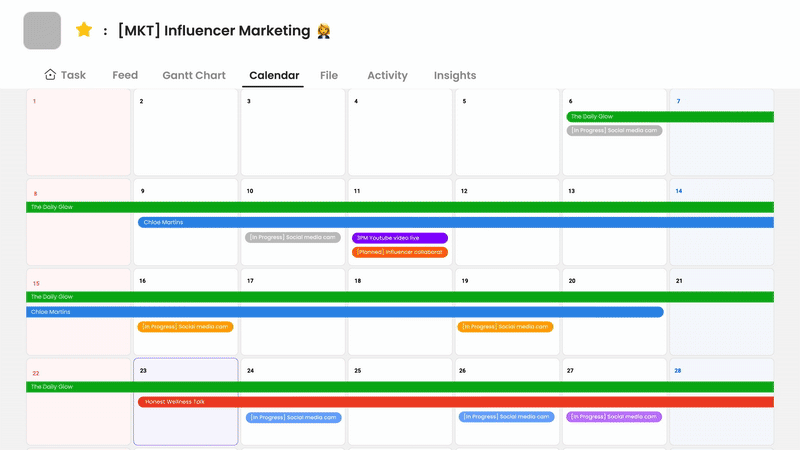
These platforms often integrate communication, task management, and file sharing to provide a central hub for collaboration on specific projects or workflows.
- Task Management & Visibility (Trello, Asana, Morningmate): Allow teams to assign tasks, set deadlines, track progress visually (Lists, timelines), and understand who is working on what.
- Centralized Project Hub (Morningmate, Asana): Combine task lists, schedules (like Gantt charts in Morningmate), file attachments, and project-specific communication (feeds/comments) in one place, providing context and reducing the need to switch between multiple apps.
- Workflow Automation: Some platforms allow automating repetitive tasks or notifications, streamlining collaborative processes.
- Morningmate Example: As an all-in-one platform, Morningmate integrates chat, project/task management (with visual timelines like Gantt charts), and file sharing (with cloud storage integration). This aims to provide a single source of truth for projects, facilitating seamless collaboration of employees by keeping conversations, tasks, and documents contextually linked within a secure environment. Its features like project feeds support asynchronous updates and discussions related to specific work items.
Building a Collaborative Workplace Culture
Tools and practices are important, but true collaboration thrives within a supportive organizational culture.
Leadership’s Role in Fostering Collaboration
- Model Collaborative Behavior: Leaders must actively demonstrate collaboration in their own interactions, breaking down silos between departments and seeking input from others.
- Champion Collaboration: Communicate the importance of collaboration as a core value and strategic priority.
- Empower Teams: Give teams autonomy and ownership over their work, trusting them to collaborate effectively to achieve goals.
- Provide Resources: Invest in the necessary tools, training, and time for teams to collaborate effectively.
- Remove Barriers: Actively identify and remove organizational obstacles or processes that hinder cross-functional teamwork.
Encouraging Cross-Functional Teams
- Structure for Collaboration: Intentionally create teams with members from different functional areas to work on specific projects or initiatives.
- Shared Objectives: Ensure these cross-functional teams have clear, shared goals that require input and expertise from all represented functions.
- Facilitate Interaction: Provide opportunities and platforms for these teams to meet, communicate, and work together easily.
Creating a Safe Space for Ideas
- Promote Psychological Safety: Foster an environment where team members feel comfortable taking risks, sharing nascent ideas, challenging the status quo, and offering constructive dissent without fear of judgment or penalty.
- Value Diverse Perspectives: Actively seek out and value different viewpoints and experiences, recognizing that diversity fuels innovation.
- Separate Ideation from Evaluation: Encourage free-flowing brainstorming initially, deferring criticism or evaluation until a later stage to avoid stifling creativity.
Final Thoughts
Effective Workplace Collaboration is not a passive outcome but an active pursuit. It requires a conscious blend of cultural reinforcement, clear processes, supportive leadership, and enabling technology. By understanding its value, implementing best practices for the collaboration of employees, leveraging appropriate digital tools like integrated platforms, and addressing the challenges head-on, organizations can unlock significant gains in productivity, innovation, and employee satisfaction. Building a collaborative culture is an ongoing investment, but one that yields powerful returns in today’s interconnected world.