Every day, organizations face inefficiencies, delays, and communication issues. Effective workflow management helps distribute tasks, personnel, and systems to ensure smooth and efficient operations. It streamlines transitions between activities, reducing errors and saving time.
Workflow management involves designing, executing, managing, and improving business activities. This includes defining team tasks, assigning responsibilities, setting guidelines, and automating processes. Companies use workflow management to speed up approvals, track projects, and manage repetitive tasks. By adopting the right strategies, organizations can boost productivity, accountability, and overall performance.
To enhance efficiency, a company must understand workflow management principles and commit to continuous improvement.
What Is Workflow Management?
Workflow management is a systematic approach to organizing and optimizing business tasks. It focuses on the efficient flow of work through established steps, aiming to eliminate bottlenecks, reduce manual labor, and ensure consistency. The workflow management process includes planning, automation, and monitoring to improve productivity. Unlike broader systems, it specifically targets task sequences rather than entire projects or complex operations.
Workflow vs. Project Management
While project management and workflow management are related, they serve different purposes. Workflow management oversees repetitive and predefined tasks, such as approvals, data entry, and ticket routing, ensuring consistency in daily operations. In contrast, project management focuses on unique initiatives with specific goals, timelines, and resources. Workflows are components of a project, while project management encompasses a wider scope, including planning, risk assessment, and team coordination.
Workflow vs. Business Process Management (BPM)
Workflow management is a subset of Business Process Management (BPM). BPM looks at the entire business process, including strategy, analysis, and long-term improvements. Workflow management focuses on executing specific task sequences within those processes. For example, BPM might redesign a company’s customer service approach, while workflow management ensures that each support ticket follows the correct procedures. Both aim for efficiency, but BPM has a broader focus, while workflow management is concerned with daily execution.
Understanding these distinctions helps businesses choose the right approach. Workflow management is ideal for routine tasks, while BPM and project management address larger, more complex needs.
Types of Workflows
Workflows can take various forms, each designed to meet specific business needs. The right workflow management process depends on how tasks should progress between individuals and systems. Some workflows follow strict sequences, while others are flexible based on changing conditions. Recognizing these types is essential for effective workflow management.
Sequential
A sequential workflow moves activities in a linear order from start to finish. Each step must be completed before the next one begins. This type is effective for fixed requirements, such as onboarding a new employee or approving a purchase. Workflow management ensures that no steps are missed.
Parallel
Parallel workflows allow multiple tasks to occur simultaneously. Different teams or systems work independently before merging their results later. This approach speeds up processes like software development, where coding, testing, and documentation can happen at the same time. Workflow management tools help coordinate these tasks to prevent conflicts or delays.
State-Machine
State-machine workflows adapt based on conditions rather than following a set path. The process shifts between various states depending on inputs or decisions made. Customer support tickets often use this model, moving from “open” to “in progress” to “resolved” based on actions taken. Managing state-machine workflows requires clear guidelines for each possible transition.
Rules-Driven
Rules-driven workflows operate according to established business logic. When specific conditions are met, certain actions are triggered automatically. Loan approvals are a common example, where applications are either approved or denied based on credit scores. Rules-driven workflows rely on accurate data and well-defined criteria to function effectively.
Choosing the right workflow type depends on the process being managed. Sequential workflows are best for step-by-step tasks, parallel workflows enhance collaboration, state-machine workflows support flexible processes, and rules-driven workflows automate decision-making. Proper implementation of workflow management ensures that each type operates smoothly and efficiently.
Key Components of a Workflow
An effective workflow management system consists of essential elements that work together to complete tasks efficiently. These components form the backbone of any workflow management process, ensuring smooth operations from start to finish. Understanding these elements allows businesses to create better workflows and enhance existing ones through effective management.
Inputs and Outputs
Inputs are the starting points of any workflow, including the information, materials, or requests that kick off the process. In workflow management, inputs can be customer orders, support tickets, or document submissions. Outputs, in contrast, are the results produced after all steps are completed, such as approved applications, processed invoices, or finalized projects. A well-structured workflow clearly defines the necessary inputs and expected outputs at each stage.
Steps and Conditions
At the heart of workflow management is the breakdown of processes into distinct steps with specific conditions. Steps represent the tasks that need to be completed, while conditions determine when and how the workflow moves forward. For example, an approval workflow may require a manager’s sign-off before proceeding to the finance department.
Effective workflow management ensures that these steps and conditions are logical, necessary, and well-documented to prevent confusion or delays.
Stakeholders and Roles
Every workflow involves individuals with defined responsibilities. Stakeholders include anyone affected by or involved in the process—employees, managers, customers, or partners. Roles clarify each person’s contribution to the workflow management process, such as requesters, approvers, or reviewers. Clearly defined roles help avoid overlaps and ensure accountability. Effective workflow management ensures that all stakeholders understand their roles and how they contribute to the overall process.
These components work together to create functional workflows. Inputs and outputs define what moves through the system, steps and conditions dictate how it progresses, and stakeholders with assigned roles facilitate execution. When these elements are aligned through careful workflow management, businesses can achieve efficient, repeatable processes that save time and reduce errors. The success of any workflow management system depends on how well these components are designed and implemented to suit each business’s specific needs.
Benefits of Workflow Management
Implementing workflow management offers significant advantages for business operations. A well-designed workflow management process enables organizations to complete tasks more quickly and accurately while improving team collaboration. These benefits make workflow management an essential tool for companies looking to optimize their daily operations.
Improved Efficiency
Workflow management streamlines processes by removing unnecessary steps and automating repetitive tasks, which reduces delays and speeds up completion times. Employees spend less time seeking approvals or clarifying next steps, as the workflow management process clearly outlines everything. Workflow management tools help track progress, ensuring that nothing is overlooked.
Greater Visibility
A strong workflow management system provides transparency at every level. Managers can see where tasks are stalled and identify steps that take too long. Employees understand their responsibilities and deadlines. This visibility empowers teams to identify bottlenecks and make necessary improvements.
Reduced Errors
Standardized workflows significantly minimize mistakes caused by unclear processes or miscommunication. Workflow management ensures that everyone follows the same steps and guidelines. Automated approvals and notifications within workflow management systems help prevent tasks from being overlooked or assigned incorrectly.
Cost Savings
Workflow management reduces unnecessary labor hours and operational waste. By streamlining approvals and eliminating redundant steps, companies can save both time and money. The workflow management process also helps avoid costly errors that may require rework. These savings can add up significantly over time.
Scalable Operations
As organizations grow, workflow management helps manage increased workloads. The same workflow can handle a higher volume without requiring additional oversight. Workflow management systems are adaptable to changing needs, allowing companies to scale operations smoothly.
These benefits highlight why workflow management is essential for modern businesses. From small teams to large corporations, implementing structured workflows leads to measurable improvements in productivity and performance. A thoughtful approach to workflow management delivers consistent results while simplifying operational management.
Common Challenges in Workflow Management
Despite the many advantages of workflow management, organizations often face challenges when implementing these systems. Recognizing these obstacles allows organizations to develop better strategies for their workflow management processes. Proper planning can prevent most issues and ensure smooth operations.
Resistance to Change
Employees may struggle to adapt to new workflow management systems. They might prefer traditional methods or feel uncomfortable with digital tools. This resistance can hinder adoption and reduce the effectiveness of workflow management solutions. Clear training and communication are vital to overcoming this challenge.
Overly Complex Workflows
Some organizations create workflow management processes that are too complicated, featuring excessive steps or approvals. This complexity can lead to delays and frustrate employees. The most effective workflow management systems prioritize simplicity while maintaining control. Regular reviews can help eliminate unnecessary complications.
Integration Challenges
Many workflow management tools have difficulty integrating seamlessly with existing business software. This can create data silos and lead to manual workarounds. Choosing workflow management solutions with strong integration capabilities can help avoid these issues. Proper IT planning is essential to ensure that all systems work together smoothly.
Best Practices for Workflow Management
Creating an effective workflow management system requires thoughtful planning and execution. By adopting proven best practices, organizations can boost efficiency and reduce disruptions. These strategies help teams optimize their workflow management processes, maximizing the benefits of their systems. Through documentation, analysis, automation, and continuous improvement, businesses can develop workflows that enhance productivity.
Document and Visualize Everything Thoroughly
Effective workflow management starts with thorough documentation. Every step, decision point, and responsibility should be clearly mapped out. Flowcharts and process diagrams allow teams to quickly understand the entire workflow. This visualization simplifies onboarding for new employees and ensures consistency across departments.
Documentation should cover all possible scenarios, including exceptions and alternative paths. Keeping these materials up to date ensures that the workflow management system accurately reflects current operations. Visual tools like swimlane diagrams can show how different roles interact within the process.
Identify Dependencies and Bottlenecks
Successful workflow management requires understanding how tasks are interconnected and where delays often occur. Analyzing dependencies reveals which steps must be completed before others can begin, preventing teams from starting tasks too early or waiting unnecessarily. The workflow management process should clearly highlight these relationships, and identifying bottlenecks is equally important.
Common bottlenecks may include approval stages, resource allocation, and departmental transitions. Workflow management tools with analytics capabilities can pinpoint these issues by tracking task durations and queue times. Addressing bottlenecks can lead to immediate improvements in overall process speed.
Automate Repetitive Tasks
Automation is one of the most powerful features of modern workflow management. Routine tasks like data entry, notifications, and standard approvals can often be automated, reducing human error and allowing employees to focus on more valuable work. The workflow management process should identify which steps are suitable for automation.
Many workflow management platforms offer built-in automation features for common business processes. When implementing automation, it’s essential to maintain human oversight for exceptions and quality control. The goal is not to eliminate human involvement entirely but to minimize tedious, repetitive tasks that add little value.
Conduct Regular Audits and Improve Workflows
Workflow management is not a one-time setup; it requires ongoing attention. Regular reviews ensure that methods align with evolving business needs. Audits should evaluate whether the management workflow supports the organization’s goals. By understanding employees’ real-world experiences, organizations can better address their challenges. Workflow management systems should include tools for continuously gathering feedback.
Improvement cycles can simplify steps, reallocate resources, or introduce new technologies. Benchmarking against similar organizations can reveal opportunities for enhancement. The most successful organizations view their workflow management as a dynamic system that adapts to changing needs.
These best practices empower organizations to implement robust and efficient workflows. When you document, you clarify. When you analyze dependencies, you eliminate delays. When you automate, you speed up processes. When you commit to continuous improvement, you stay ahead. Implementing these strategies requires time and investment but yields significant rewards in streamlined operations and improved outcomes.
Organizations that master these workflow management techniques gain a substantial competitive advantage. Successful workflow management is an ongoing practice that evolves alongside the organization.
Workflow Management Systems & Tools
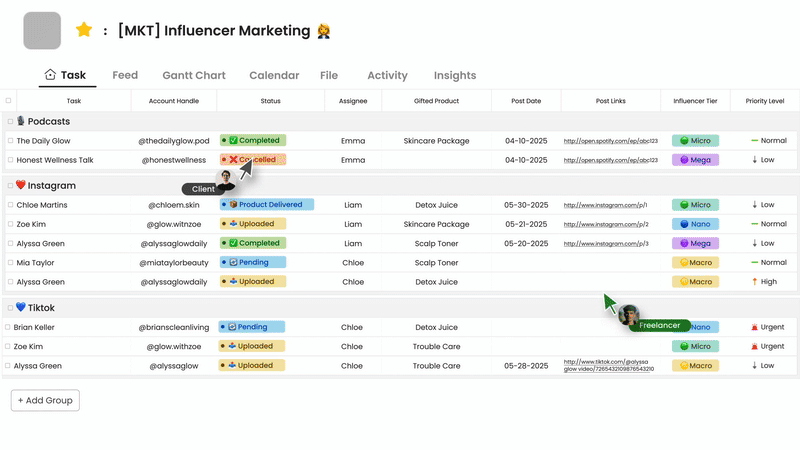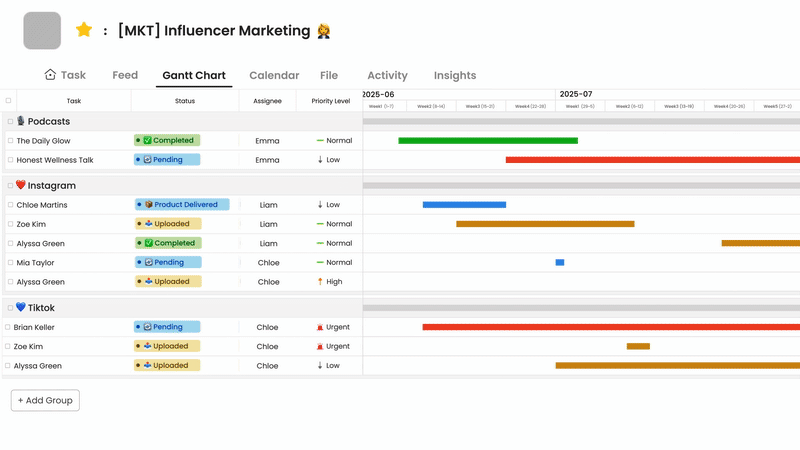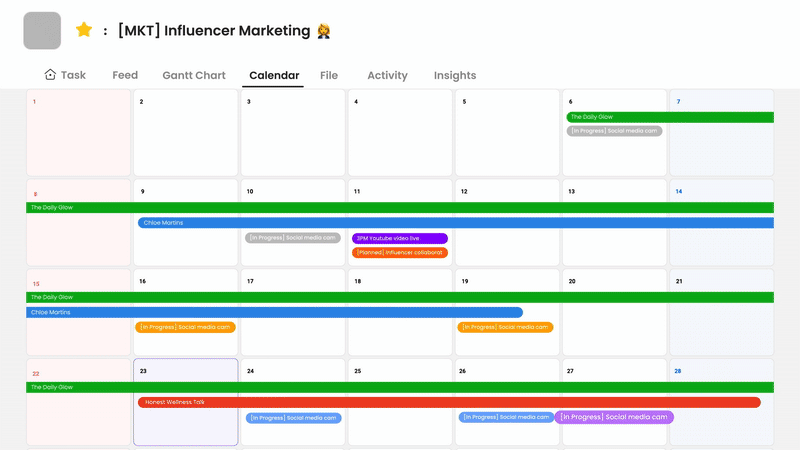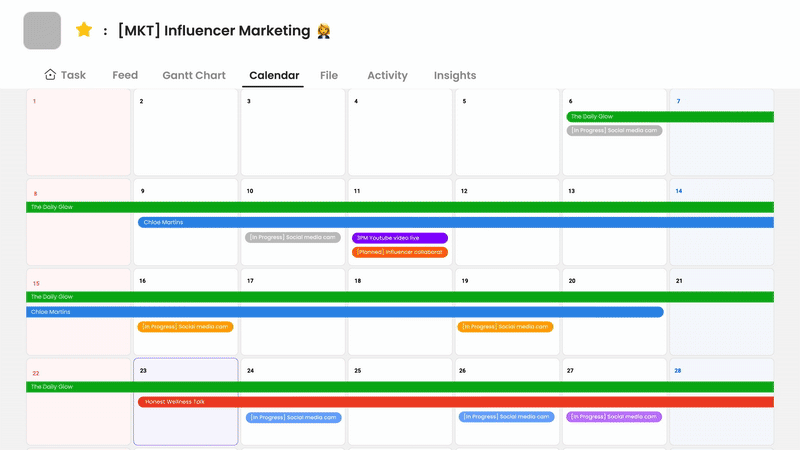
Choosing the right tools for managing workflows can greatly enhance team collaboration. Morningmate offers an innovative approach to workflow management, designed to help teams stay organized and efficient. Unlike complex systems that often add to the workload, Morningmate simplifies daily responsibilities while ensuring everything runs smoothly.
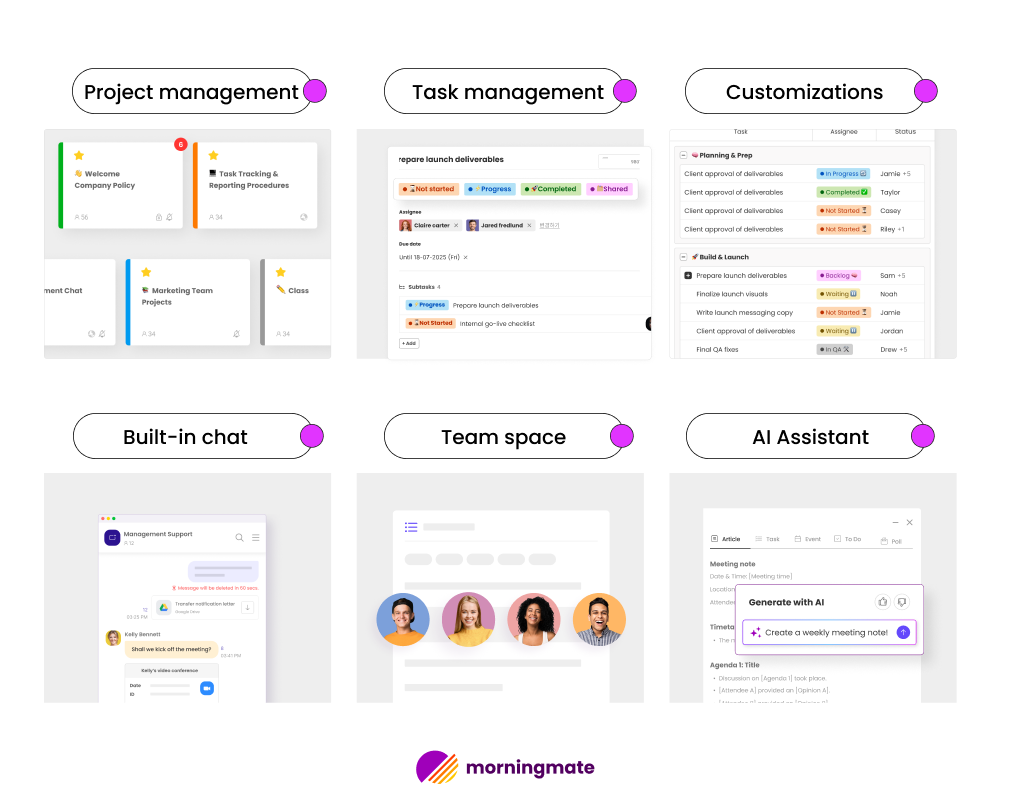
Morningmate understands that each team has its unique way of working. The platform provides a centralized space for teams to manage tasks, deadlines, and communication. Its user-friendly design allows for easy visibility of what needs attention without overwhelming the users. The tool enables teams to track project progress while automatically organizing routine tasks, making it suitable for both structured processes and flexible teamwork.
What sets Morningmate apart is its seamless integration into daily work routines. The system provides timely reminders and updates without causing disruptions. Managers can quickly assess project statuses, while team members receive clear instructions about their responsibilities. Morningmate integrates with other tools teams use, consolidating information in one place and saving valuable time that would otherwise be spent switching between applications.
How to Visualize and Optimize Workflows
Visualizing workflows helps teams understand how tasks progress through various stages. Clear visual representations make it easier to identify inefficiencies and enhance processes. Optimization translates these insights into necessary changes that save time and reduce errors, fostering smoother and more efficient workflows.
Mapping Current Processes
Start by outlining each step in your existing workflow. Simple flowcharts work best, showing who is responsible for each task and how information flows between individuals. Include decision points where tasks may diverge. Visualizing everything often uncovers unnecessary steps or delays that may not have been obvious before.
Identifying Improvement Areas
Look for bottlenecks where work accumulates or slows down. Common problem areas include approval processes, team transitions, or repetitive manual tasks. Additionally, evaluate steps that do not clearly add value to the final outcome. These areas often present the best opportunities for optimization.
Testing and Implementing Changes
Make incremental adjustments rather than complete overhauls. Start by eliminating one bottleneck or automating a single repetitive task. Monitor whether this change produces positive results before making further modifications. Successful optimizations should enhance workflow speed without compromising quality. Continuously update the visual map as you refine the workflow.
Monitoring Results
After implementing changes, observe how the workflow performs over time. Assess whether tasks are completed more quickly and with fewer errors. Gather feedback from team members about whether the new process is easier to navigate. Regular check-ins are essential for identifying new issues early and ensuring workflows remain efficient.
Effective workflow visualization and optimization is an ongoing effort, not a one-time task. As business requirements evolve, workflows should adapt accordingly. Keeping visuals current and consistently seeking improvements helps maintain long-term efficiency.
Conclusion
Successful workflow management transforms team operations by introducing clarity, efficiency, and structure to everyday processes. Whether through visualization, optimization, or utilizing tools like Morningmate, the goal remains the same: to eliminate bottlenecks, minimize wasted effort, and ensure that work flows smoothly from start to finish. By documenting workflows, identifying inefficiencies, and implementing targeted enhancements, organizations can boost productivity while maintaining flexibility.
The key lies in continuous refinement—regularly evaluating what works and adjusting as needs change. With the right strategy, workflow management evolves into more than just a system; it becomes a competitive advantage that empowers teams to work smarter, collaborate more effectively, and achieve consistent results with less friction.