In today’s fast-moving business environment, many organizations are adopting agile methods to deliver products faster and more efficiently. A key position within agile teams is the scrum master. Whether you are an aspiring project manager, a developer, or just curious about modern software development, knowing what a scrum master does can open up exciting career opportunities for you.
What Is a Scrum Master?
A scrum master acts as a facilitator and coach for agile development teams using the Scrum framework. They don’t directly build the product but ensure the team has everything needed to work effectively. The scrum master supports the team by removing obstacles, facilitating meetings, and helping everyone adhere to Scrum principles.
Unlike traditional project managers who often control team activities, scrum masters adopt a servant leadership style. They guide without commanding, support without micromanaging, and empower teams to self-organize and make decisions. This shift in leadership style makes the scrum master role unique within agile methodologies.
Learn about the 6 popular project management methodologies >
Agile Context and Role Origin
The scrum master role originated from the Scrum framework, introduced in the 1990s by Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherland. Inspired by rugby, where a “scrum” signifies a coordinated team effort to advance the ball, this agile framework emphasizes collaboration, iterative development, and continuous improvement.
Within the broader agile ecosystem, Scrum offers a structured yet flexible approach to product development. The scrum master ensures that this framework is effectively implemented and continuously improved. They act as guardians of the Scrum process, helping teams transition from traditional waterfall methodologies to more dynamic, responsive approaches.
What Does a Scrum Master Do?
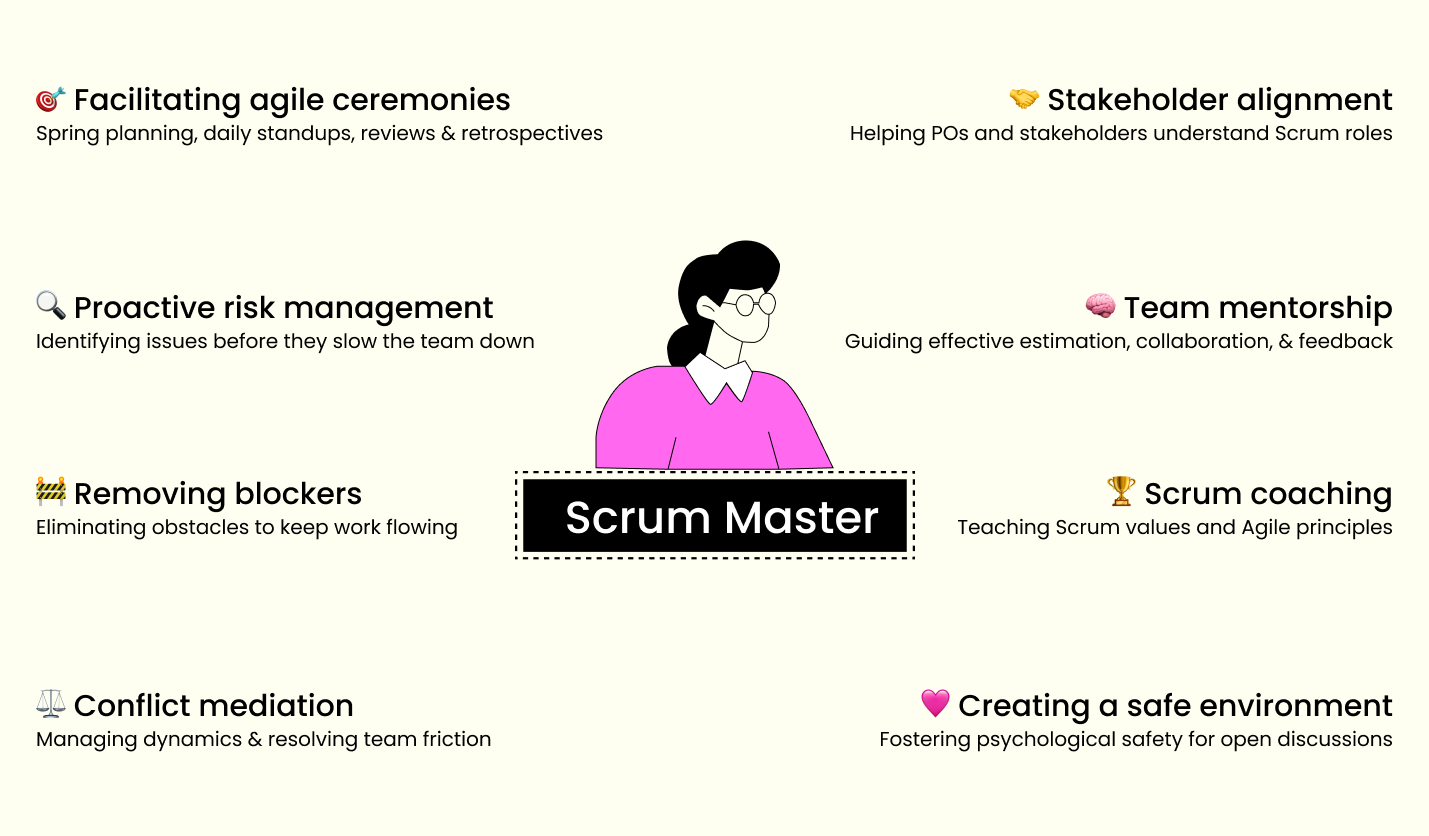
Facilitates Agile Ceremonies
One of the primary responsibilities of scrum masters is to orchestrate various Scrum ceremonies that keep teams aligned and productive. These include sprint planning sessions, where teams decide on tasks for the upcoming sprint; daily standups to ensure synchronization; sprint reviews to demonstrate completed work; and retrospectives focused on continuous improvement.
During these ceremonies, the scrum master serves as a neutral facilitator, ensuring discussions remain productive and time-bound. They create a safe environment for team members to express concerns, celebrate successes, and identify areas for improvement. This facilitation goes beyond running meetings; it involves understanding team dynamics, managing conflicts, and ensuring every voice is heard.
Removes Blockers and Fosters Team Flow
Scrum masters excel at identifying and eliminating obstacles that hinder team progress. Whether it’s a technical issue, a dependency on another team, or an organizational policy causing friction, they work diligently to resolve these challenges. This may involve negotiating with other departments, escalating issues to management, or finding creative solutions.
In addition to removing existing blockers, experienced scrum masters proactively identify potential issues before they affect the team. They stay aware of upcoming challenges, resource constraints, and external dependencies that could disrupt sprint goals. This proactive approach helps maintain consistent team velocity and prevents last-minute scrambles.
Coaches the Team on Scrum Principles
Education and coaching are significant aspects of a scrum master’s daily responsibilities. They help team members understand and embrace Scrum values such as commitment, courage, focus, openness, and respect. This coaching is practical, providing guidance on how to apply these principles in real work situations.
Scrum masters also mentor individuals on agile practices, from effective estimation techniques to collaborative problem-solving methods. They observe team interactions, offer feedback, and suggest improvements that align with agile principles. This coaching extends to stakeholders and product owners, helping them understand their roles within the Scrum framework.
Scrum Master vs. Other Roles
Scrum Master vs. Project Manager
The difference between scrum masters and traditional project managers can be confusing for those new to agile environments. Project managers typically concentrate on planning, controlling, and delivering projects within specific scope, time, and budget limits. They manage resources, timelines, and stakeholder expectations through detailed project plans and status reports.
In contrast, scrum masters prioritize team empowerment and process improvement over project control. They do not assign tasks or manage individual performance; instead, they create an environment that allows teams to self-organize and deliver value. While project managers might ask, “Are we on schedule?” scrum masters ask, “How can we help the team work more effectively?”
Scrum Master vs. Product Owner
Scrum masters and product owners collaborate closely but have different roles within Scrum teams. Product owners define what gets built; they manage the product backlog, prioritize features, and make decisions about product direction based on business value and customer needs.
Scrum masters focus on how work is accomplished rather than what work is done. They ensure the team adheres to best practices, maintains a sustainable pace, and continuously improves its processes. While product owners represent the voice of the customer and business stakeholders, scrum masters advocate for the team and the Scrum process.
Scrum Master vs. Agile Coach
While scrum masters and agile coaches share many similarities, agile coaches typically operate at a broader organizational level. Scrum masters concentrate on individual teams, whereas agile coaches may work with multiple teams, departments, or entire organizations to facilitate agile transformations.
The role of an agile coach often includes strategic planning, organizational change management, and executive coaching.
Key Scrum Master Skills
Communication and Facilitation
Strong communication skills are essential for effective scrum mastery. Scrum masters must clearly convey complex concepts, facilitate challenging conversations, and ensure smooth information flow throughout the organization. They should adapt their communication style to suit different audiences, from technical team members to executive stakeholders.
Facilitation skills extend beyond running meetings efficiently. Great scrum masters foster environments where creativity thrives, conflicts are resolved constructively, and teams make decisions collaboratively. They employ various facilitation techniques to generate ideas, build consensus, and keep participants engaged during lengthy working sessions.
Servant Leadership Mindset
The philosophy of servant leadership is central to the scrum master role. This approach prioritizes the needs of team members and emphasizes their growth and development. Servant leaders lead by example, show vulnerability, and share power with their teams rather than hoarding it.
This mindset requires scrum masters to set aside their egos and focus on enabling others’ success. They celebrate team achievements instead of seeking personal recognition and make decisions based on what is best for the team and organization, even when it poses personal challenges.
Agile Process Knowledge and Conflict Resolution
A deep understanding of agile methodologies and Scrum principles allows scrum masters to guide teams through complex situations. This knowledge is not just theoretical; it includes practical experience with various tools, techniques, and approaches that help teams consistently deliver value.
Scrum Master in the Scrum Framework
Place in the Team
Within the Scrum framework, scrum masters work alongside development teams and product owners as one of three key roles. This trio creates a balanced system where each role has distinct responsibilities but collaborates toward common goals. The development team builds the product, the product owner defines requirements, and the scrum master ensures the process functions effectively.
Relationship with Stakeholders
Scrum masters act as bridges between development teams and various stakeholders throughout the organization. They help translate business requirements into actionable development tasks and communicate team progress and challenges to interested parties. This translation works both ways; they also help stakeholders understand team constraints and agile principles.
Managing stakeholder expectations requires diplomatic skills and a deep understanding of both business needs and technical realities. Scrum masters often protect teams from excessive external pressure while ensuring legitimate business concerns are addressed appropriately.
When Do You Need a Scrum Master?
Ideal Team Size and Complexity
Most experts agree that teams of 5-9 members benefit most from dedicated scrum masters. Smaller teams may share scrum master responsibilities among members, while larger teams might require multiple scrum masters or additional support roles. The complexity of the product, organizational maturity, and team experience level also influence this decision.
Transitioning to Agile Environments
Organizations moving from traditional project management approaches to agile methodologies particularly benefit from skilled scrum masters. These transitions involve significant cultural shifts, process changes, and mindset adjustments that require careful guidance and support.
How to Become a Scrum Master
Education and Background
Aspiring scrum masters come from various fields, including software development, project management, business analysis, quality assurance, and even non-technical areas. While having technical knowledge can be beneficial, it is not always necessary. What truly matters are strong interpersonal skills, problem-solving abilities, and a genuine desire to help teams succeed.
Top Scrum Certifications
Several certification programs can validate your knowledge and skills as a scrum master. The Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) from Scrum Alliance is one of the most recognized entry-level certifications. The Professional Scrum Master (PSM) from Scrum.org offers a more rigorous assessment-based approach.
For those in larger organizations, Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) certifications, such as the SAFe Scrum Master, provide valuable insights into implementing agile practices on an enterprise scale. The Disciplined Agile Scrum Master (DASM) certification offers a broader view of various agile methodologies beyond just Scrum.
Career Growth and Salary Outlook
Scrum masters typically have several paths for career advancement. Some may progress to senior scrum master roles, supporting multiple teams or complex products. Others may transition into agile coaching positions, assisting organizations with broader agile transformations. Additional career options include product ownership, project management, and team leadership.
Salary expectations can vary widely based on location, experience, and industry. Entry-level scrum masters may earn between $73,000 and $124,000 annually, while experienced professionals in major metropolitan areas can earn $120,000 to $150,000 or more. The increasing demand for agile expertise continues to drive competitive compensation packages.
Common Challenges Scrum Masters Face
Resistance to Agile
One of the primary challenges scrum masters face is resistance to agile practices from team members, stakeholders, or organizational leaders. This resistance often arises from fear of change, past negative experiences, or misunderstandings about agile principles.
To overcome this resistance, scrum masters need patience, education, and the ability to demonstrate value through small wins. They must act as change agents, clearly communicating the benefits of agile methods while addressing legitimate concerns constructively.
Misunderstood Responsibilities
Many organizations struggle to grasp the true role of scrum masters, leading to confusion and unrealistic expectations. Some may see them as project managers in disguise, while others expect them to serve as technical leads or administrative assistants.
Balancing Servant Leadership and Authority
Implementing the servant leadership model can be challenging, especially in organizations with strong hierarchical cultures. Scrum masters must influence without authority, guide without controlling, and lead without commanding—skills that may not come naturally to everyone.
Achieving this balance requires emotional intelligence, patience, and strong relationship-building skills. Successful scrum masters earn respect through service rather than demanding it through positional power.
Is Scrum Master the Right Career for You?
To determine if the scrum master role aligns with your career goals, conduct an honest self-assessment. Do you find fulfillment in helping others succeed rather than seeking personal recognition? Are you comfortable with ambiguity and constant change? Do you have the patience to guide teams through learning processes instead of providing direct answers?
If you’re ready to embark on your scrum master journey, start by exploring certification programs, joining local agile meetups, and seeking mentorship from experienced practitioners in your network. The agile community is welcoming and supportive of newcomers who show a genuine interest in learning and growing.