Do you ever feel like your project data is scattered across multiple platforms? Spreadsheets, emails, sticky notes—keeping track of everything can waste time and lead to mistakes. If this sounds familiar, it’s time to consider a Project Management Information System (PMIS). In simple terms, a PMIS serves as the central hub for your project. This specialized software consolidates all essential details—tasks, budgets, risks, and documents—into one real-time platform.
Why is this important? Without a PMIS, teams can spend up to 20% of their time searching for information, according to McKinsey. Errors increase, and decision-making slows down. However, with a PMIS, you can automate routine tasks, identify risks early, and keep everyone on the same page.
By the end of this guide, you’ll understand how a PMIS streamlines planning, execution, and reporting—whether you’re preparing for the PMP exam or managing projects directly. Let’s eliminate the chaos.
What is PMIS?
If disorganized project data is hindering your team, a Project Management Information System (PMIS) is the answer. This centralized software replaces various tools with a single command center for all project activities.
PMIS Meaning and Definition
A Project Management Information System is specialized software that collects, processes, and shares vital project data. It serves as a single source of truth for tasks, resources, budgets, and risks.
Unlike basic tools, a true PMIS automates workflows and supports decision-making throughout all project phases. It eliminates manual tracking and ensures that every stakeholder has access to real-time updates. This technology is essential for efficiency in complex projects.
What Does PMIS Stand For?
PMIS stands for Project Management Information System. Each part of this acronym highlights its function: Project refers to initiatives aimed at achieving specific goals, Management involves planning and control, Information relates to the flow of data, and System indicates the use of integrated technology.
Recognizing the meaning of PMIS assists teams in understanding its role in standardizing processes. It is officially recognized in frameworks such as the PMP (Project Management Professional) curriculum as an essential factor in project success.
Project Information Management vs. PMIS
Project Information Management (PIM) is the process of organizing project data, which includes establishing filing systems and approval workflows. A Project Management Information System (PMIS) is the digital tool that automates this process. You can think of PIM as “what we do” and PMIS as “how we do it.”
While PIM can make use of basic applications, a dedicated PMIS provides advanced features such as risk dashboards and budget alerts. For a more structured execution, Project Management Information System solutions are more effective than generic methods.
Why PMIS Matters in Project Management
Understanding what a Project Management Information System is reveals its critical importance. It transforms chaotic projects into streamlined operations.
PMIS in the PMP Framework
The Project Management Institute (PMI) highlights the PMIS as essential within the PMP framework. The PMBOK® Guide identifies it as a core tool for processes like monitoring project work.
PMP candidates must understand how a Project Management Information System supports planning and control. It automates tracking against baselines, a crucial skill for PMP certification. This system is vital for achieving success in professional project management.
Real-World Use Cases of PMIS
PMIS software addresses real challenges across various industries. In construction, it tracks schedules, materials, and compliance using tools like Procore. Marketing teams leverage PMIS platforms like Wrike to manage campaigns, assets, and budgets in real time.
These real-world examples demonstrate that a PMIS helps prevent delays and cost overruns. It transforms data into actionable insights for quicker decision-making.
Key Functions of a Project Management Information System
Now that we understand the importance of PMIS, let’s explore its core functions. These capabilities make it essential for modern project execution and form its operational backbone.
Planning and Scheduling Support
PMIS software revolutionizes project planning. It creates work breakdown structures to divide complex goals into manageable tasks. The PMIS then generates interactive timelines that illustrate task dependencies. Automatic critical path calculations identify high-impact tasks.
Baselines capture approved plans for future comparison. When changes occur, the PMIS instantly shows their impact on the schedule. This replaces error-prone manual scheduling, ensuring teams always know their next priority and can identify resource conflicts before assignments.
Resource and Budget Management
PMIS manages two critical constraints: people and money. Its resource database tracks skills and availability across projects. The PMIS prevents over-allocation through visual workload charts. Budget tools capture estimates and establish cost baselines.
Real-time expense tracking compares actual spending against forecasts. This PMIS project management feature immediately flags budget variances. It automates earned value calculations like CPI and SPI, allowing financial decisions to be based on live data rather than outdated spreadsheets.
Communication and Documentation
Centralized information is a defining feature of PMIS. All documents—charters, plans, deliverables—are stored in a single version-controlled repository. The project management information system links discussions directly to tasks or files.
@mentions notify specific team members, and automated alerts keep stakeholders updated on milestones or approvals. No more sifting through email chains for updates. Remote teams remain equally informed, and audit trails show who made changes and when.
Risk and Issue Tracking
What is a PMIS without effective risk management? It maintains a dynamic risk register with probability and impact scores. The PMIS software assigns risk owners and tracks mitigation progress. Issues are logged with severity levels and resolution deadlines.
Automated triggers alert teams about schedule delays or budget overruns. Change requests follow customizable approval workflows, shifting from reactive firefighting to proactive prevention. Historical data aids in predicting future threats.
Real-Time Reporting & Dashboards
PMIS refers to actionable visibility. Custom dashboards present live key performance indicators (KPIs), including schedule variance, budget health, and milestone completion. The drill-down features provide detailed task data. The PMIS can generate reports—such as status updates, resource utilization, and risk exposure—with a single click.
Automated distribution guarantees that stakeholders receive timely insights. Trends are easily identified without the need for manual data analysis, enabling decisions to be made based on current information rather than outdated assumptions.
PMIS Throughout the Project Lifecycle
Understanding the functions of a project management information system (PMIS) reveals how it operates. Now, let’s explore when it adds value across all five phases of a project.
Initiation Phase
In the initiation phase, the PMIS serves as a secure repository for essential documents. It stores the project charter and business case, while also capturing initial stakeholder information in a centralized register.
Early risk assessments are recorded for future reference. This phase illustrates the PMIS’s role as a single source of information, helping teams avoid the misplacement of critical startup documents.
Planning Phase
During the planning phase, the PMIS becomes indispensable. It helps create the work breakdown structure and project schedule, allocates resources, and establishes budget baselines.
Risk registers are updated with mitigation strategies, and communication plans are stored and shared through the PMIS, creating a master roadmap for the entire team.
Execution Phase
The PMIS truly shines during execution. Teams can update task progress in real time, recording actual hours and expenses against the budget.
Documents such as designs and test results are version-controlled, and communication tools keep discussions linked to deliverables. The PMIS effectively turns plans into action.
Monitoring & Controlling Phase
In this phase, the PMIS is critical for tracking progress. It compares actual performance to baselines using real-time data and calculates variances, such as the schedule performance index (SPI).
Risk triggers activate alerts for immediate action, and change requests follow established approval workflows. Reports provide stakeholders with real-time health checks.
Closure Phase
The PMIS systematically captures project history. Final deliverables receive digital sign-offs within the system, and lessons learned are documented for future reference.
Resources are formally released in the PMIS, and contracts and project archives are stored permanently, transforming experience into organizational knowledge.
Benefits of Using a PMIS
Having explored the PMIS in action across project phases, its tangible benefits become evident. These advantages significantly enhance team operations.
Enhanced Decision Making
PMIS tools provide real-time insights, replacing guesswork with live dashboards that display progress.
This software highlights risks before they escalate, allowing managers to compare actual performance against baselines instantly. Data-driven decisions replace delayed reactions.
Improved Team Collaboration
PMIS platforms break down silos, enabling remote teams to access the same documents and updates. Version control prevents conflicting edits, while centralized discussions and @mentions ensure quick responses. This alignment reduces the need for endless meetings.
Accelerated Project Delivery
PMIS features streamline workflows. Automated scheduling adjusts timelines dynamically, resource leveling prevents bottlenecks, and budget tracking curbs overspending early. These capabilities can reduce manual reporting time by 30% (Gartner), leading to quicker project completions.
Increased Data Accuracy
A true PMIS minimizes errors by providing a single source of data, eliminating conflicts associated with spreadsheets. Automated timesheets and expense logs reduce typos, and the system maintains audit trails, fostering trust in consistent numbers among stakeholders.
Challenges of PMIS Implementation
Despite its clear advantages, adopting PMIS software can present challenges. Recognizing these early can help prevent implementation failures.
Team Resistance
Resistance to change can hinder PMIS rollouts. Employees may prefer familiar tools like spreadsheets, and inadequate training can exacerbate this challenge.
Complex interfaces can intimidate non-technical users. Leaders must clearly communicate the reasons for adoption and provide ongoing support along with simplified workflows.
Tool Overlap
Existing systems frequently conflict with PMIS software. For instance, accounting tools may replicate budgeting features, while communication applications might overlap with PMIS collaboration functions, resulting in uncertainty about where to update data.
“Shadow IT” can occur when teams use unauthorized tools, and integration gaps may require manual data transfers, which can elevate the risk of errors.
Customization Challenges
The flexibility of a PMIS solution can be limited. Off-the-shelf software may not align with unique processes, and complex customizations can significantly raise costs.
Overly modified systems may break during updates, and building a custom PMIS requires substantial IT resources. Striking a balance between specific needs and adaptability is essential.
Examples of PMIS Software
Understanding the challenges of PMIS helps in evaluating potential solutions. Here are six leading PMIS software platforms that are revolutionizing project execution today.
Morningmate
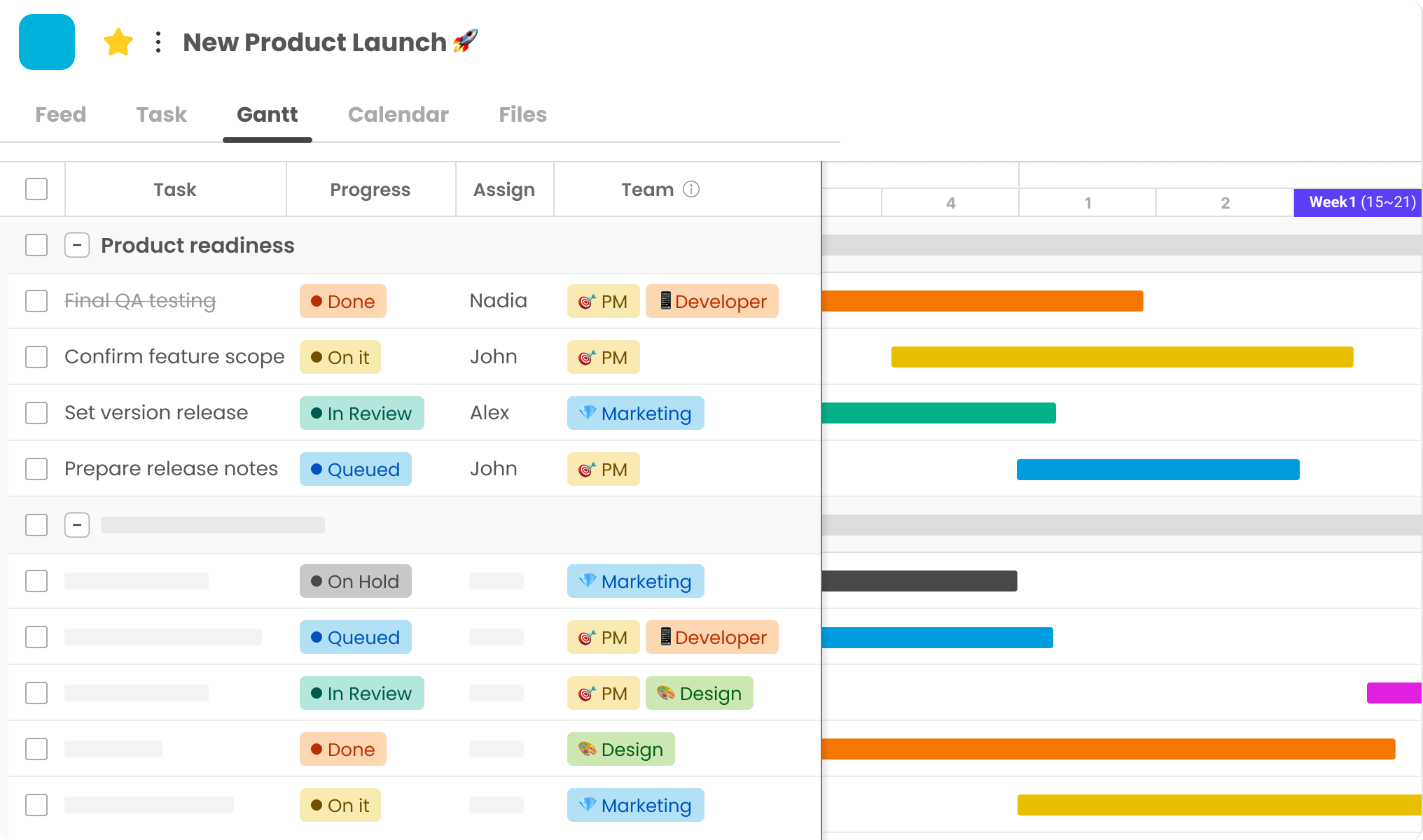
Morningmate is a visually engaging and user-friendly collaboration platform designed for project-driven teams. Its intuitive interface supports visual timelines and task management, helping teams stay on track without complexity.Its Gantt chart and customizable workflow offer robust planning features.
The platform excels in real-time messaging and centralized file sharing, enabling teams to manage communication, documents, and deadlines all in one place. Ideal for marketing teams and SMEs, Morningmate offers an affordable, easy-to-adopt solution that lowers the barriers typically associated with project management systems.
Wrike
Wrike offers enterprise-level PMIS software that balances structure and flexibility. It effectively manages complex workflows with customizable request forms and approval paths. This PMIS solution excels in workload management across multiple projects.
Advanced reporting transforms data into actionable insights for stakeholders. Wrike integrates seamlessly with marketing tools and CRMs, making it a scalable option for mid-sized to large teams that require robust PMIS capabilities.
ProjectManager
ProjectManager provides strong planning-focused PMIS tools. Its interactive Gantt charts simplify scheduling with drag-and-drop functionality. Real-time dashboards visually track progress across portfolios.
Resource management features effectively prevent team overallocation. This PMIS platform connects planning to execution seamlessly. ProjectManager is well-suited for traditional project management teams that need powerful project management information system software without unnecessary complexity.
Microsoft Project
Microsoft Project remains the industry standard for complex PMIS system scheduling. Its in-depth critical path analysis is ideal for large-scale construction or engineering projects. When paired with Project Online, it offers portfolio-level PMIS project management insights.
Tight integration with Power BI enables advanced analytics. This project management information system excels in environments where precise scheduling is essential. Its steeper learning curve is best suited for mature project management offices (PMOs).
Monday.com
Monday.com serves as a flexible PMIS software Work OS. Its customizable databases adapt to project tracking, CRMs, or inventory management. No-code automations streamline repetitive tasks across workflows.
Visual dashboards make status updates straightforward. This PMIS platform integrates with over 40 tools natively. Monday.com is perfect for dynamic teams seeking a versatile project management information system that goes beyond traditional PM.
Smartsheet
Smartsheet combines the familiarity of spreadsheets with PMIS functionality. Users comfortable with grids can benefit from automated workflows and reports. Its control center enforces governance across large organizations.
Robust forms collect standardized project data. This PMIS solution is ideal for operations teams transitioning from manual tracking. Enterprise features support secure scaling of project management information system needs.
How to Choose the Right PMIS Software
With numerous PMIS software options available, selecting the right one requires careful evaluation. Focus on these key areas.
Feature Checklist
Identify the essential functions for your projects. Every project management information system should handle scheduling and resource management. Prioritize features that align with your workflow, such as PMIS project management, risk tracking, or agile boards.
Avoid tools that introduce unnecessary complexity. Ensure mobile access and flexible reporting are available. Scalability is crucial to prevent future tool changes.
Cloud vs. On-Premise Options
Cloud PMIS software typically offers lower costs and instant updates, making it suitable for remote teams needing access from anywhere. On-premise PMIS system installations provide complete data control but require IT resources.
Most modern teams prefer cloud-based project management information system solutions for their flexibility. However, compliance requirements may necessitate on-premise solutions for sensitive industries.
Security & Compliance
Check for encryption and access controls in any PMIS. Ensure the PMIS project management information system complies with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA. Look for certifications such as SOC 2 or ISO 27001. Review backup policies and breach response plans. Vendor transparency regarding data storage locations is essential.
Integration with Existing Tools
The PMIS software should integrate seamlessly with your current tools. Test integrations with email, file storage (e.g., SharePoint), and accounting systems.
Native connectors reduce manual work. Avoid PMIS system options that require custom coding for basic integrations. A smooth data flow prevents duplicate entries and errors.
Final Thoughts: The Role of PMIS in Modern Teams
Choosing the right PMIS software underscores its strategic importance. A project management information system serves as the operational backbone for contemporary project teams.
It goes beyond simple task tracking. The PMIS unifies data, people, and processes into one dynamic hub. This PMIS system eliminates fragmented tools and information chaos, providing teams with real-time visibility into progress, risks, and resources.
For project leaders, PMIS project management means proactive control. Decisions are based on live data rather than outdated reports. Stakeholders can trust consistent, auditable information. The PMIS project management information system transforms lessons learned into future success.
Ultimately, what is a PMIS? It represents the difference between reactive efforts and strategic delivery. Invest wisely to enhance your project execution.