Project management provides teams with a structured approach to complete tasks on time and within budget. However, many projects fail due to inadequate planning. To address this issue, teams need effective project management best practices.
Establishing clear goals, choosing the right methodology, and ensuring stakeholder alignment are crucial for successful project management. By following proven strategies—whether for a small task or a large initiative—teams can significantly increase their chances of success. These key strategies lead to smoother implementation and better project outcomes.
When teams apply the right techniques, they can avoid delays, minimize risks, and keep stakeholders satisfied. By focusing on practical steps, teams can sidestep common pitfalls and achieve their objectives.
What Are Project Management Best Practices?
Project management best practices are tested methods that enhance efficiency, mitigate risks, and help achieve goals. Successful projects depend on effective planning, clear communication, and resource management. By adopting these best practices, you can expect fewer delays, reduced costs, and improved results.
While different industries may use various approaches, the fundamental principles remain consistent. Whether you choose Agile, Waterfall, or a hybrid model, effective project management practices will help you succeed. Selecting the right strategies that align with your project’s needs and allow for flexibility is essential.
Why Best Practices Matter in 2025
As projects become increasingly complex, adhering to industry best practices in project management is vital. Today, teams often work remotely, utilize advanced tools, and face tighter deadlines. Without a formalized approach, project timelines can easily slip.
Effective project planning best practices enable teams to adapt to new challenges. They clarify roles, establish realistic timelines, and ensure proper risk management. Companies that overlook these methods waste time correcting avoidable mistakes. In 2025, businesses must implement efficient workflows to remain competitive, and strong project management is key to achieving that.
Common Mistakes When Skipping Best Practices
Many projects fail because teams neglect project management best practices. A significant mistake is poor goal-setting. Without clear objectives, teams lack direction, leading to wasted efforts. Another common error is inadequate communication. When team members fail to share updates, issues can go unnoticed until it’s too late.
Ignoring risk management is another frequent oversight. Unexpected challenges will always arise, but teams lacking solid project management practices are often unprepared, resulting in budget overruns and missed deadlines. Additionally, some teams overly rely on tools without establishing proper processes. While technology can be beneficial, it cannot replace effective planning and collaboration.
By following project management best practices, teams can avoid these pitfalls. Structured methods enable teams to deliver projects more quickly, with fewer errors and greater stakeholder satisfaction. The right approach ultimately saves time, money, and reduces stress in the long run.
12 Essential Project Management Best Practices
Project managers rely on proven strategies to guide projects from inception to completion. The top twelve project management best practices enable organizations to deliver projects on time, within budget, and with high quality. While each project is unique, many principles apply across various industries. Implementing effective project management practices minimizes risks, boosts efficiency, and keeps stakeholders satisfied.
Successful teams blend careful planning with adaptability. They follow structured methods while remaining open to change. Below are twelve key project management best practices that significantly enhance project success. Each practice includes clear explanations and practical tips for implementation to help teams achieve outstanding results.
1. Define a Clear Business Case
Every successful project starts with a well-defined purpose. A business case outlines the project’s justification, detailing expected benefits, costs, and risks. It addresses essential questions: Why is this project necessary? What problems will it solve? How will success be measured?
To create a strong business case, gather input from key stakeholders. Collect data on market needs, financial projections, and potential challenges. The document should be concise yet comprehensive enough to guide decision-making. A solid business case aligns the team and prevents scope creep later in the project.
Regularly revisiting the business case throughout the project ensures alignment with original objectives. If market conditions or business priorities shift, the business case may need adjustments. This living document serves as the project’s guiding star, keeping everyone focused on delivering real value.
2. Develop a Concise Project Brief
The project brief translates the business case into actionable guidance for the team. This 1-2 page document summarizes critical information, including objectives, success criteria, timelines, budgets, and key stakeholders. Unlike lengthy project plans, the brief provides quick reference points for daily decision-making.
A well-crafted brief clearly states what is in scope and, equally important, what is out of scope. It identifies potential risks and constraints upfront. The brief should be accessible to all team members and stakeholders for reference throughout the project.
Teams should collaborate across departments to develop the brief, ensuring diverse perspectives are considered from the outset. The brief should be updated to reflect significant changes, which should be documented and communicated.
3. Create a Realistic, Detailed Project Plan
A comprehensive project plan breaks the project into phases with milestones. It includes a work breakdown structure, resource allocation, risk assessment, and quality control. Successful plans balance desired outcomes with what is feasible.
When creating the plan, involve those who will execute the work. Frontline team members often provide the most accurate estimates for task durations. The plan should account for task dependencies and include buffer time for unexpected delays.
Modern project planning incorporates agile elements, even in traditional waterfall projects, allowing for flexibility while maintaining overall structure. Regular plan reviews (at least monthly) help teams adapt to changing circumstances without losing sight of the end goal.
4. Communicate Clearly and Consistently
Effective communication is crucial for project success. Teams must establish various channels for quick updates, formal reports, issue resolution, and stakeholder feedback. The communication plan should outline the frequency, formats, and responsibilities for each channel.
Daily stand-up meetings (15 minutes max) help teams align on immediate priorities. Weekly status reports provide high-level updates to executives, while monthly deep-dive sessions facilitate strategic discussions. All communication should be purposeful and avoid unnecessary noise.
In modern projects, technology enhances communication. Real-time discussions can occur on collaboration platforms like Slack or Teams, while project management software offers visibility into progress. However, teams should balance digital tools with face-to-face interactions, as personal connections strengthen working relationships.
5. Monitor for Scope Creep
Scope creep can quietly undermine projects through gradual requirement expansion. Effective scope management starts with a clearly defined baseline in the project charter. Any proposed changes should undergo a formal evaluation process that considers impacts on timelines, budgets, and resources.
Teams can establish a change control board to review modification requests. Each change should be documented with its justification, estimated impact, and approval status. Even minor changes can accumulate, so nothing should be implemented without proper evaluation.
Regular scope audits help identify unauthorized changes early. Comparing current work against original requirements keeps the project focused. When additional features are necessary, teams should formally adjust timelines and budgets rather than trying to absorb the extra work.
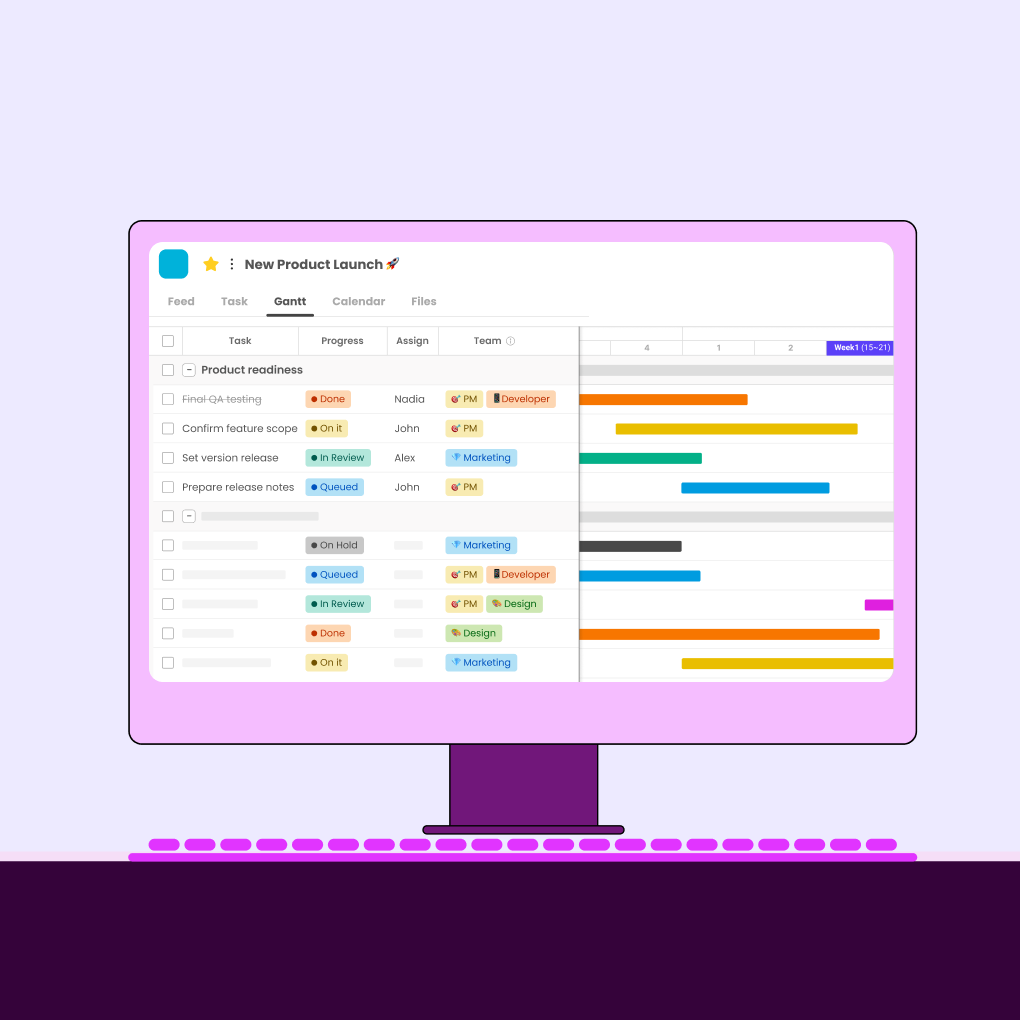
6. Keep the Schedule Visible and Updated
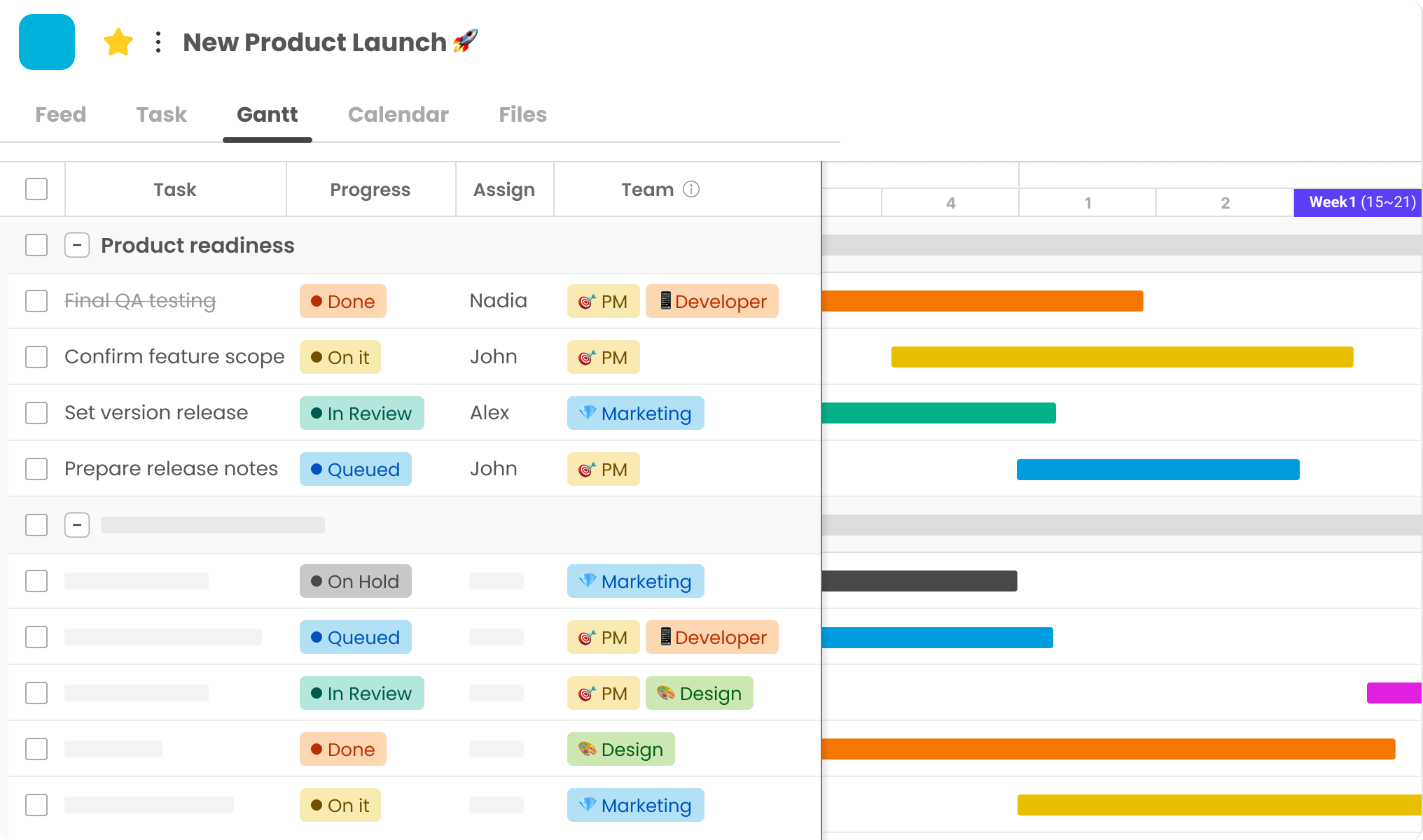
A dynamic, accessible project schedule serves as the team’s shared reality. It should display task owners, deadlines, dependencies, and progress indicators. The schedule must be updated frequently to reflect actual progress rather than remaining an overly optimistic initial plan.
Visual scheduling tools like Gantt charts help teams understand workflow sequences. Color-coding different project phases or departments enhances readability. The schedule should be prominently displayed in team spaces (physical or virtual) and reviewed in every status meeting.
If delays occur, the schedule should be revised to reflect new completion dates. Corrective action is necessary if the root cause of the delay is identified. An accurate, up-to-date schedule enables better decision-making.
7. Use a Centralized Collaboration Tool
Disconnected communication and scattered documents lead to confusion and inefficiency. A single digital workspace consolidates all project information—tasks, documents, discussions, and schedules. The right tool depends on project complexity and team preferences but should always enhance workflow.
Key features to look for include:
- Task assignment and tracking
- Document storage and version control
- Calendar integration
- Mobile accessibility
- Customizable views for different roles
Teams should establish guidelines for tool usage to maintain organization, including naming conventions for files, standardized status indicators, and protocols for tagging team members. Proper training ensures all members can use the tool effectively.
8. Track All Project Data and Tasks
Comprehensive tracking provides visibility into project health. Beyond basic task completion, teams should monitor quality metrics, budget consumption, risk triggers, and stakeholder satisfaction. This data enables evidence-based decision-making rather than relying on gut feelings.
Automated tracking reduces administrative burdens. Many project management tools offer reports on schedule variances, budget performance, and resource utilization. Teams should identify key performance indicators (KPIs) early and monitor them.
Regularly reviewing data helps identify patterns. For example, patterns of missed deadlines in a specific workstream can be addressed promptly. Historical data aids in designing realistic projects in the future.
9. Keep Documentation Organized
Organized documentation saves time and effort. A logical folder structure with consistent naming conventions makes files easy to find. Sensitive data can be protected with access controls in cloud storage.
Essential documentation includes:
- Project charter and business case
- Meeting minutes and decision logs
- Change requests and approvals
- Quality assurance records
- Vendor contracts and service agreements
Teams should establish documentation rules early, including what needs to be recorded, where it’s stored, and who owns it. Regular audits of documentation ensure compliance. Maintaining project records allows others to benefit from your work.
10. Plan for Setbacks and Adjustments
Experienced project managers understand that surprises are inevitable. Prepare in advance to avoid being caught off guard. Set aside a reserve budget, identify alternative suppliers, and cross-train team members on critical tasks.
Risk management should not be limited to the planning phase. Regular risk review sessions help identify new threats as the project progresses. The team should categorize risks by probability and impact, focusing mitigation efforts on high-priority items.
When challenges arise, the team should focus on solutions rather than assigning blame. A structured approach to problem-solving—defining the problem, analyzing root causes, listing options, and implementing fixes—typically yields better outcomes. Learning from failures helps prevent future issues.
11. Engage Stakeholders Throughout
Stakeholder engagement should extend beyond the kickoff and final delivery. Different stakeholders require varying levels and types of involvement. A stakeholder analysis matrix helps identify who needs what information and when.
Key engagement strategies include:
- Regular progress briefings for executives
- Working sessions with subject matter experts
- User testing and feedback loops for end-users
- Vendor performance reviews
Effective engagement builds trust and surfaces concerns early. Teams should document all stakeholder input and demonstrate how it is being addressed. Transparent communication helps manage expectations and prevents disappointment at project completion.
12. Conduct Post-Project Retrospectives
A project is not truly finished until the lessons learned are documented. A structured retrospective reviews what went well, what didn’t, and how to improve in the future. This discussion should be free of blame and focus on processes rather than individuals.
Retrospectives are most effective when:
- Held shortly after project completion
- Include representatives from all functional areas
- Concentrate on actionable improvements
- Document outcomes for future reference
Teams should identify 2-3 key improvements to implement in the next project. Monitoring whether these changes lead to better results completes the cycle of continuous improvement. Capturing lessons learned helps prevent repeating the same mistakes.
Best Practices in Project Planning
Effective project planning lays the groundwork for success. A lack of clear direction can hinder even the most skilled teams. Adopting popular project planning best practices keeps teams organized and on track while avoiding costly errors. Good planning ensures proper resource allocation and stakeholder alignment throughout the project.
The best plans strike a balance between structure and flexibility. They provide clear guidance while allowing for necessary adjustments. Adhering to project management best practices during the planning phase helps prevent issues later on. Teams that invest time in thorough planning complete projects more quickly and with fewer complications.
Aligning Plans with Goals
Every project plan should align with the project’s main objectives. Teams must understand what success looks like before establishing timelines. This means reviewing the project brief and business case first. Plans that do not align with goals waste time and resources.
A key project management practice is setting measurable targets. Plans should outline clear outcomes instead of vague goals (like “improve customer satisfaction”). For instance, a more specific outcome would be “reduce the time taken to close a support ticket by 30%.” Clear metrics make it easier to track progress and adjust plans as needed.
Regular check-ins help maintain alignment. Comparing ongoing work with initial goals allows teams to identify deviations early. Plans may need to change if business priorities or market conditions shift. When goals and plans are connected, the project delivers real value.
Utilizing Templates and Roadmaps
Using templates can save time and ensure consistency across projects. Many organizations have standard templates available. These tools help teams adhere to project management best practices.
Roadmaps offer a high-level overview of the project journey. They visually represent key milestones, dependencies, and deliverables, illustrating how the team’s work fits into the larger picture. This makes it easier to explain the project plan to stakeholders.
While templates and roadmaps are helpful, customizing them for each project is essential. A one-size-fits-all approach rarely works. Teams should adapt standard tools to meet their specific needs while maintaining quality project management practices.
Involving the Right Team Early
The best project plans incorporate input from those who will execute the work. Involving team members in planning sessions leads to more realistic timelines and better solutions. Frontline workers often identify potential issues that managers might overlook.
Early involvement also fosters commitment. When team members contribute to the plan, they take greater ownership of the results. This is one of the most effective project management practices. Engaged teams are more motivated to overcome challenges and meet deadlines.
Key stakeholders should also participate in planning discussions. Their insights can help avoid costly changes later. For example, including IT staff early in a software project can identify technical constraints before development begins. Cross-functional planning sessions lead to stronger, more actionable plans.
Good planning requires effort but pays off throughout the project. Teams that follow these project management best practices start strong and maintain momentum. Clear goals, useful tools, and early collaboration set the stage for success from day one. A solid planning approach makes execution smoother and outcomes more predictable.
Industry Standards and Frameworks to Consider
Choosing the right project management approach significantly impacts outcomes. Various frameworks and standards exist to guide teams, each with strengths suited to different situations. Understanding these project management best practices helps organizations select methods that fit their needs. The right framework provides structure while allowing for necessary flexibility.
Established standards help teams avoid common pitfalls and work more efficiently. They offer proven processes for planning, execution, and control. Following recognized project management best practices ensures consistency and improves success rates across projects. Teams should evaluate options to find what works best for their specific goals and work environment.
Agile, Waterfall, Scrum: When to Use What
Different projects require different management approaches. Waterfall is ideal for projects with clear, unchanging requirements. It follows a linear sequence from planning to execution, making it suitable for construction or manufacturing. Teams complete each phase before moving to the next, which aids in budgeting and scheduling.
Agile methods are better suited for projects that require flexibility. Software development and creative projects often use Agile because requirements may change. This approach breaks work into short cycles called sprints, allowing for regular adjustments. Scrum is a popular Agile framework that employs daily stand-ups and sprint reviews to keep teams aligned.
Hybrid approaches combine elements of both methods. Many teams blend Waterfall’s structure with Agile’s adaptability. The choice depends on project complexity, team size, and the expected level of change. Good project management practices involve selecting the framework that best matches the project’s nature rather than forcing a single approach on all work.
Learn about popular project management methods >
PMBOK and PMP Standards
PMBOK serves as a comprehensive guide for managing various types of projects. It outlines processes, best practices, and terminology used across industries. Many organizations adopt PMBOK standards as a foundation for effective project management. The framework consists of five process groups and ten knowledge areas.
PMP certification indicates a professional’s ability to manage projects successfully. Certified PMP Managers understand how to apply PMBOK principles in practice. Obtaining this certification requires experience and passing a rigorous exam. Companies often prefer managers with PMP certification for large projects due to their adherence to project planning best practices.
While PMBOK is valuable, teams should adapt it to their needs. The standards serve as a starting point, not a rigid set of rules. Often, combining PMBOK with other frameworks like Agile proves more effective. The key is to implement these best practices for project management to enhance results while remaining realistic.
Learning these standards and frameworks helps teams work more efficiently. Adopting the right approach reduces confusion, increases efficiency, and improves project success rates. Organizations that implement and learn best practices in project management perform better across all projects.
Tools That Support Project Management Best Practices
The right tools facilitate adherence to project management best practices. They help teams stay organized, communicate effectively, and track progress efficiently. While processes and planning are crucial, good software integrates everything in one place. Many options are available, but the best tools align with how teams actually work while supporting effective project management practices.
Modern solutions extend beyond basic task lists. They integrate scheduling, document sharing, and team collaboration, eliminating the need to switch between multiple applications. The most effective tools adapt to various project approaches, whether teams use Agile, Waterfall, or hybrid methods. Choosing software that fits existing workflows helps teams adopt project management best practices more easily.
Morningmate: All-in-One Collaboration and PM Tool
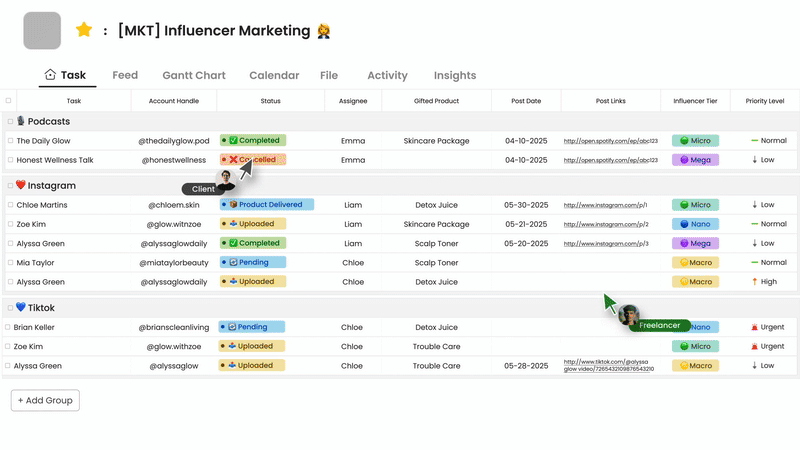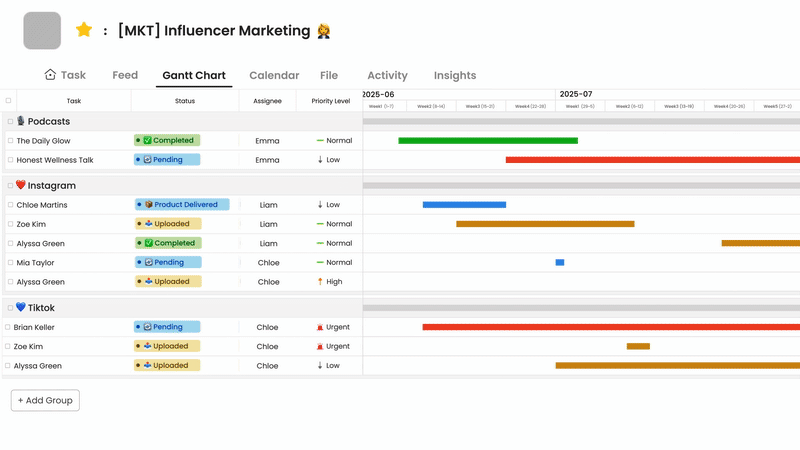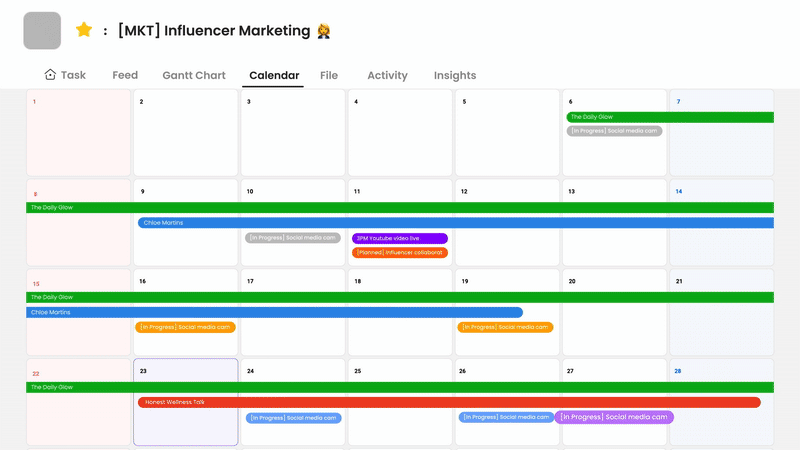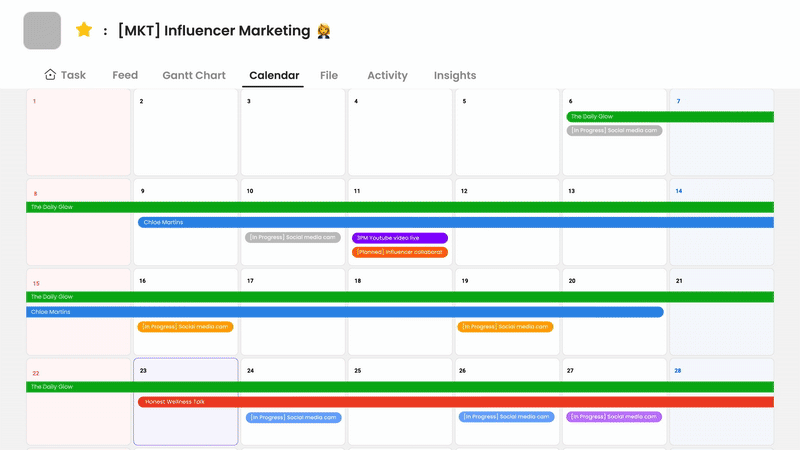
Morningmate combines project management with team collaboration in a single platform. It supports key project management best practices through features like task assignment, progress tracking, and file sharing. The tool’s user-friendly interface makes it easy for teams to adopt without extensive training.
What sets Morningmate apart is its focus on both projects and people. It includes spaces for work discussions alongside task management, keeping communication connected to actual work items. Teams can create timelines, set priorities, and monitor deadlines while maintaining visibility across all projects.
The tool is well-suited for remote and hybrid teams. Its notification system ensures everyone stays updated without the need for constant meetings. Morningmate exemplifies how modern software can embed effective project management practices into daily work. By reducing tool switching and keeping everything organized, it allows teams to focus on delivering results rather than managing workflows.
Final Thoughts: Adopting Best Practices for Long-Term Success
Implementing project management best practices is not about following rigid rules—it’s about building habits that lead to consistent results. The most successful teams combine proven methodologies with the right tools, like Morningmate, to streamline collaboration and execution. These solutions embed structure into daily work while maintaining the flexibility teams need to adapt.
Tools like Morningmate demonstrate how technology can reinforce good project management practices without adding complexity. By centralizing tasks, communication, and documentation, such platforms help teams focus on delivering value rather than managing workflows. However, even the best tools only enhance—they don’t replace—the need for solid planning, clear communication, and stakeholder alignment.
Lasting improvement comes when teams pair the right frameworks with the right technology. Morningmate’s all-in-one approach shows how modern solutions can simplify best practises for project management, making them easier to adopt and sustain. Organizations that combine these tools with disciplined processes see compounding benefits: fewer missed deadlines, better resource utilization, and more successful projects.